Abstract
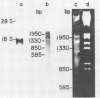
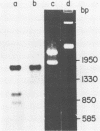
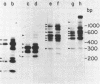
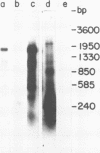
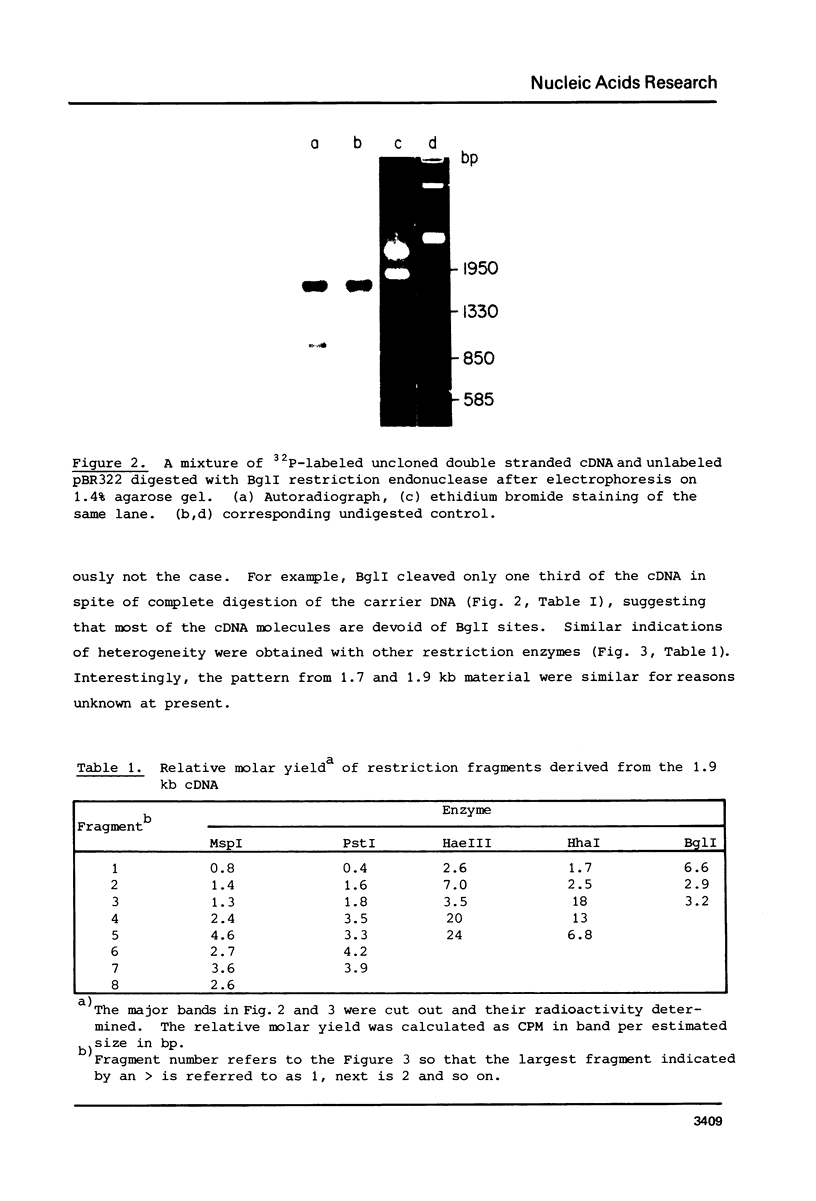
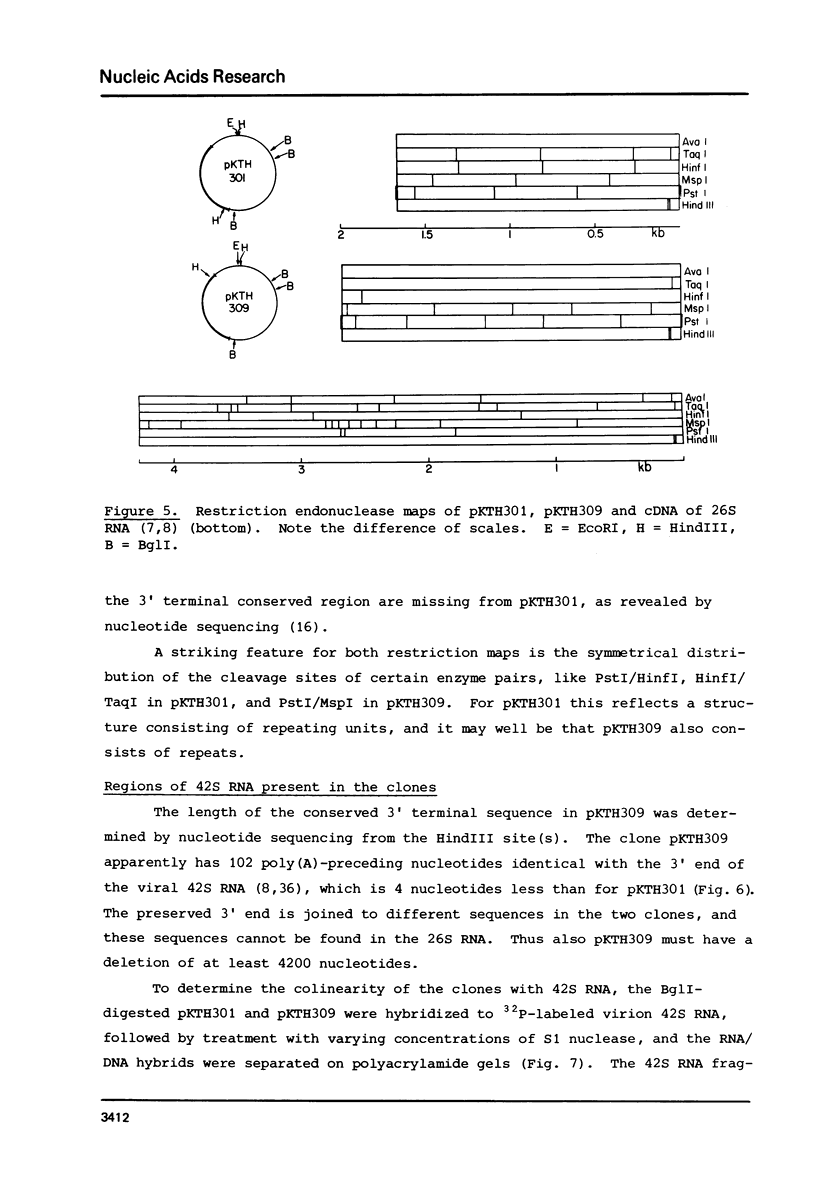
The 18S defective interfering RNA of Semliki Forest virus has been reverse transcribed to cDNA, which was shown to be heterogeneous by restriction enzyme analysis. After transformation to E.coli, using pBR322 as a vector, two clones, pKTH301 and pKTH309 with inserts of 1.7 kb and 2 kb, were characterized, respectively. The restriction maps of the two clones were different but suggested that both contained repeating units. At the 3' terminus, pKTH301 had preserved 106 nucleotides and pKTH309 102 nucleotides from the 3' end of the viral 42S genome. The conserved 3' terminal sequence was joined to a different sequence in the two clones, and these sequences were not derived from the region coding for the viral structural proteins. The DI RNAs represented by the two clones are generated from the viral 42S RNA by several noncontinuous internal deletions, since the largest colinear regions with 42S RNA are 320 nucleotides in pKTH301, and 430 and 340 nucleotides in pKTH309. All these fragments had unique RNase T1 oligonucleotide fingerprints, suggesting that they were derived from different regions of 42S RNA.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Kennedy S. I. Defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest Virus: structural differences between standard virus and defective-interfering particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):383–395. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton B. T. Defective interfering particles of Semliki Forest virus generated in BHK cells do not interfere with viral RNA synthesis in Aedes albopictus cells. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):534–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of cdna coding for Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):236–241. doi: 10.1038/288236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. The capsid protein of Semliki Forest virus has clusters of basic amino acids and prolines in its amino-terminal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Morser J., Uomala P., Käri5AAINEN L. Simultaneous translation of structural and nonstructural proteins from Semliki-forest-virus RNA in two eukaryotic systems in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):167–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen P. G. Separation and isolation of DNA fragments using linear polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):305–319. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback D. B., Angerer L. M., Davidson N. Improved methods for the formation and stabilization of R-loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2499–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Structure and replication of alpha-viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:15–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagley P., Clayton D. A. Transcriptional mapping of the ribosomal RNA region of mouse L-cell mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2947–2965. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Comparative studies of the 3'-terminal sequences of several alpha virus RNAs. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90499-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F. 5'-Terminal nucleotide sequence of Semliki forest virus 18S defective interfering RNA is heterogeneous and different from the genomic 42S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):115–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. The nucleotide sequences of the 5'-terminal T1 oligonucleotides of Semliki-Forest-virus 42-S and 26-S RNAs are different. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(3):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Jay E., Wu R. Terminal labeling and addition of homopolymer tracts to duplex DNA fragments by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):101–116. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Gomatos P. J. Replication of semliki forest virus: polyadenylate in plus-strand RNA and polyuridylate in minus-strand RNA. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):446–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.446-464.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V. Defective interfering particles of togaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;86:35–66. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67341-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski E. H., Szybalski W. A comprehensive molecular map of bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1979 Nov;7(3-4):217–270. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Flavell R. A. A method for the recovery of DNA from agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2321–2332. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Gross H. S. Replicative form of Semliki Forest virus RNA contains an unpaired guanosine. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):754–756. doi: 10.1038/282754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Localization of the 26-S RNA sequence on the viral genome type 42-S RNA isolated from SFV-infected cells. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]