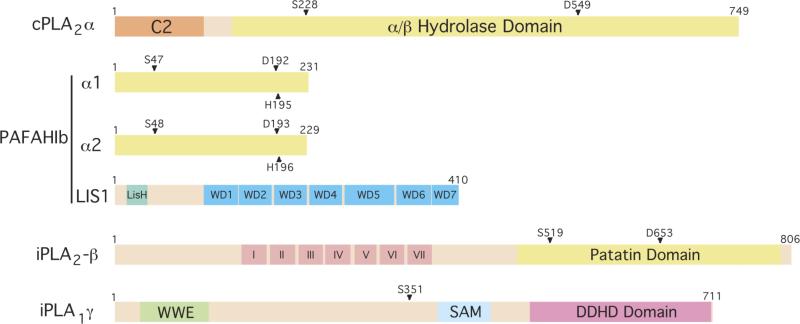
Figure 1. Domain structures of Golgi- and ERGIC-associated PLA enzymes.
cPLA2α contains a large α/β hydrolase domain with residues S228 and D549 comprising the active site dyad. It also contains a C2 Ca2+-binding domain that is necessary for translocation to Golgi membranes. PAFAH Ib is comprised of α1 and α2 homo- or heterodimers together with LIS1. The indicated residues form the active site triad. iPLA2–β contains a patatin lipase domain, with an active site at S519, and seven ankyrin repeats (I-VII). iPLA1γ contains an S351 residue, which when mutated to alanine (A) abolishes catalytic activity, a DDHD2 domain that is conserved with iPLA1β, a WWE domain predicted to mediate protein-protein interactions in ubiquitination and ADP-ribosylation systems, and a SAM domain (sterile alpha motif) that can mediate both homo- and hetero-oligomerization.