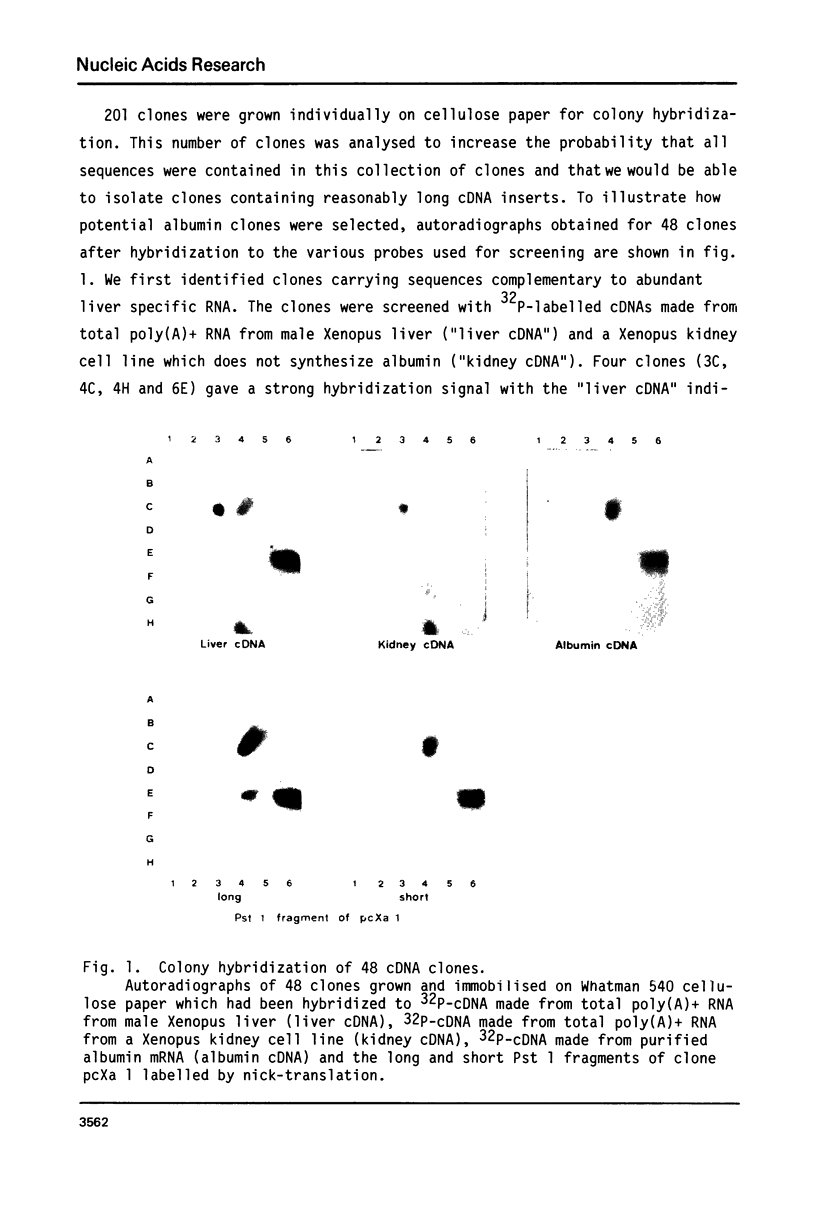
Abstract
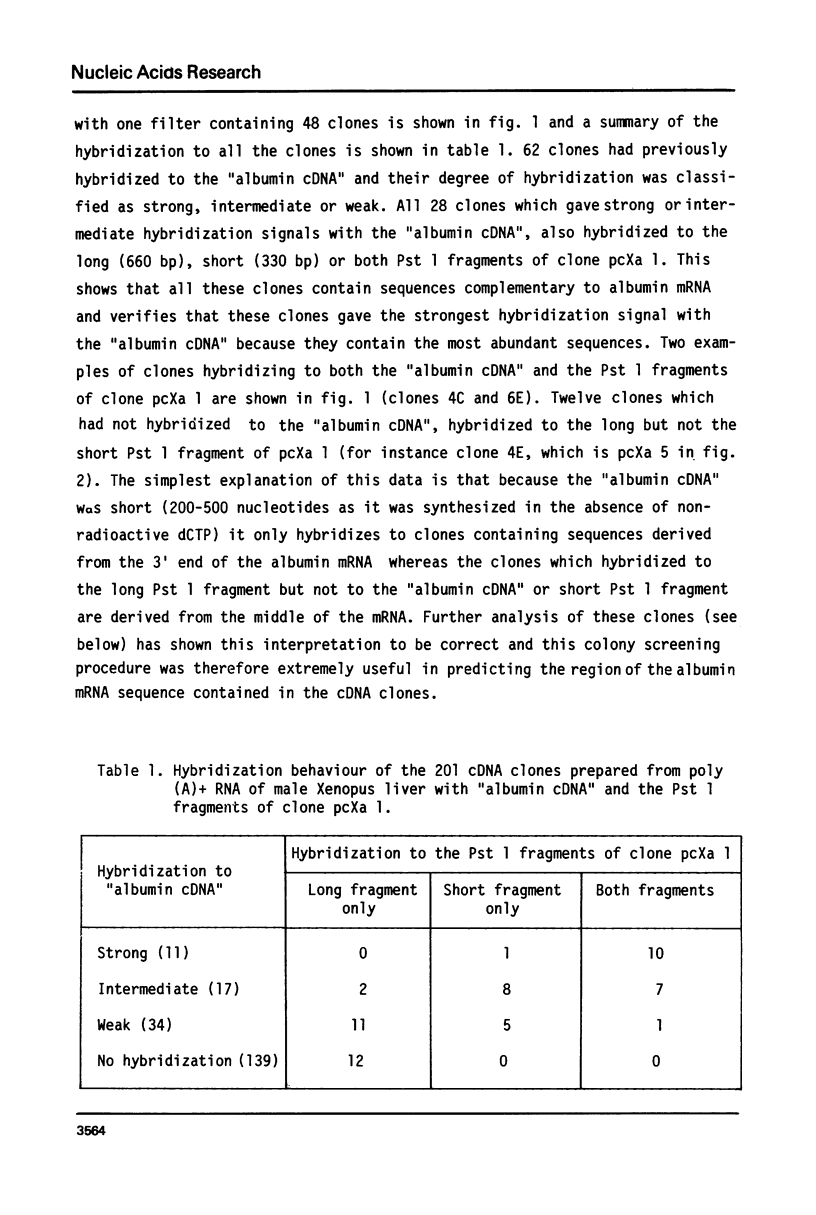
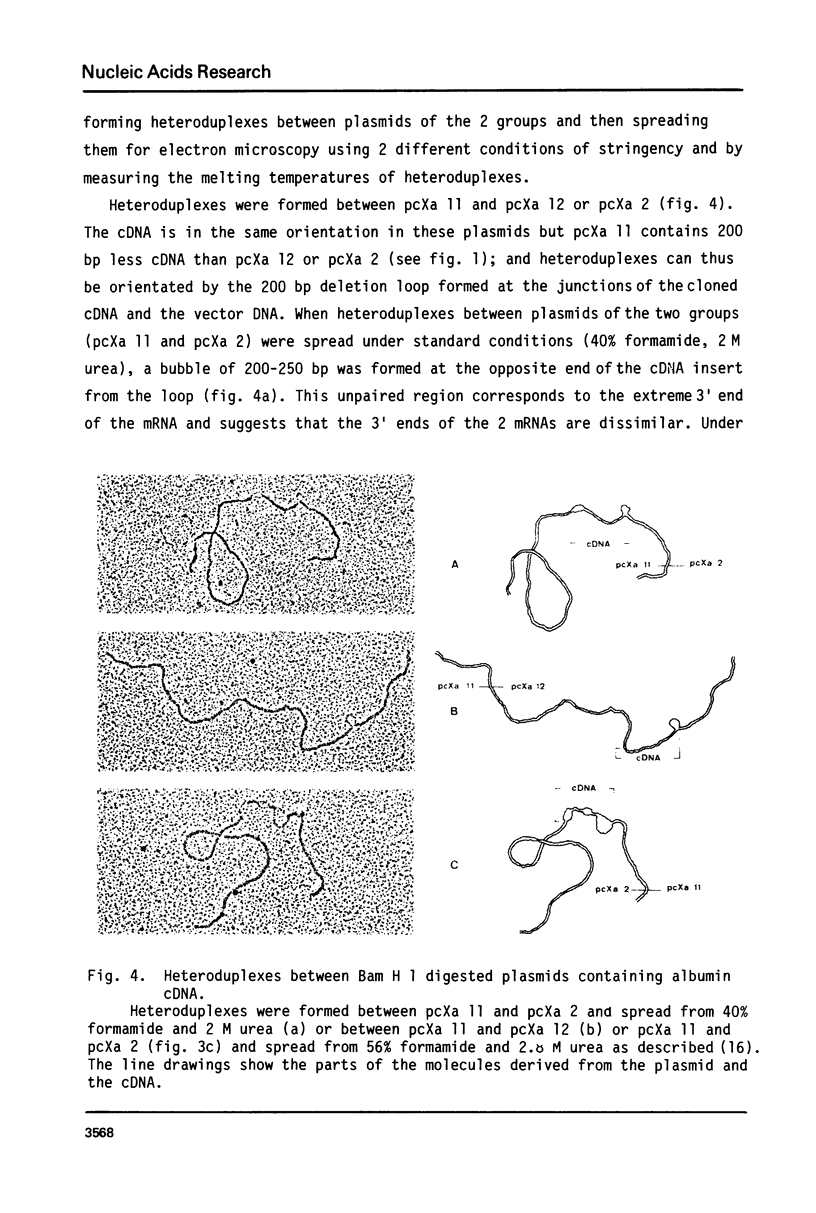
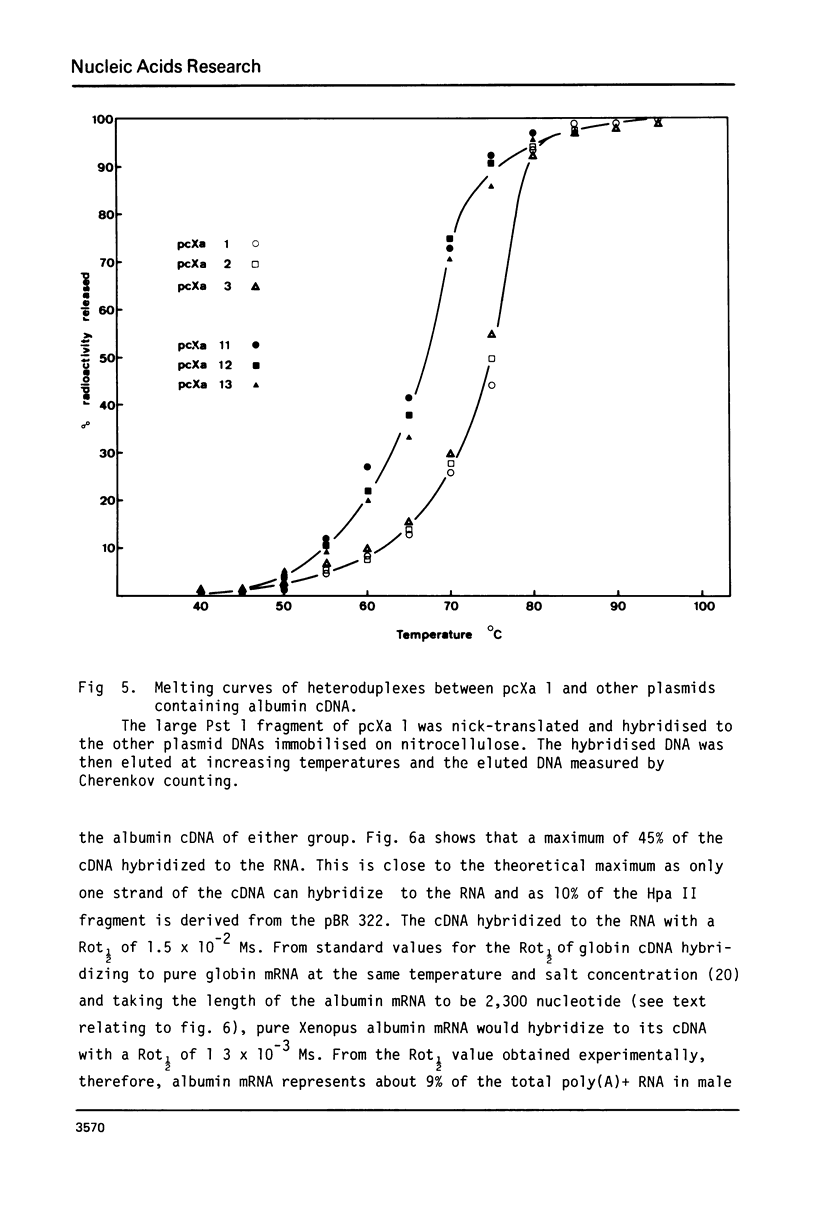
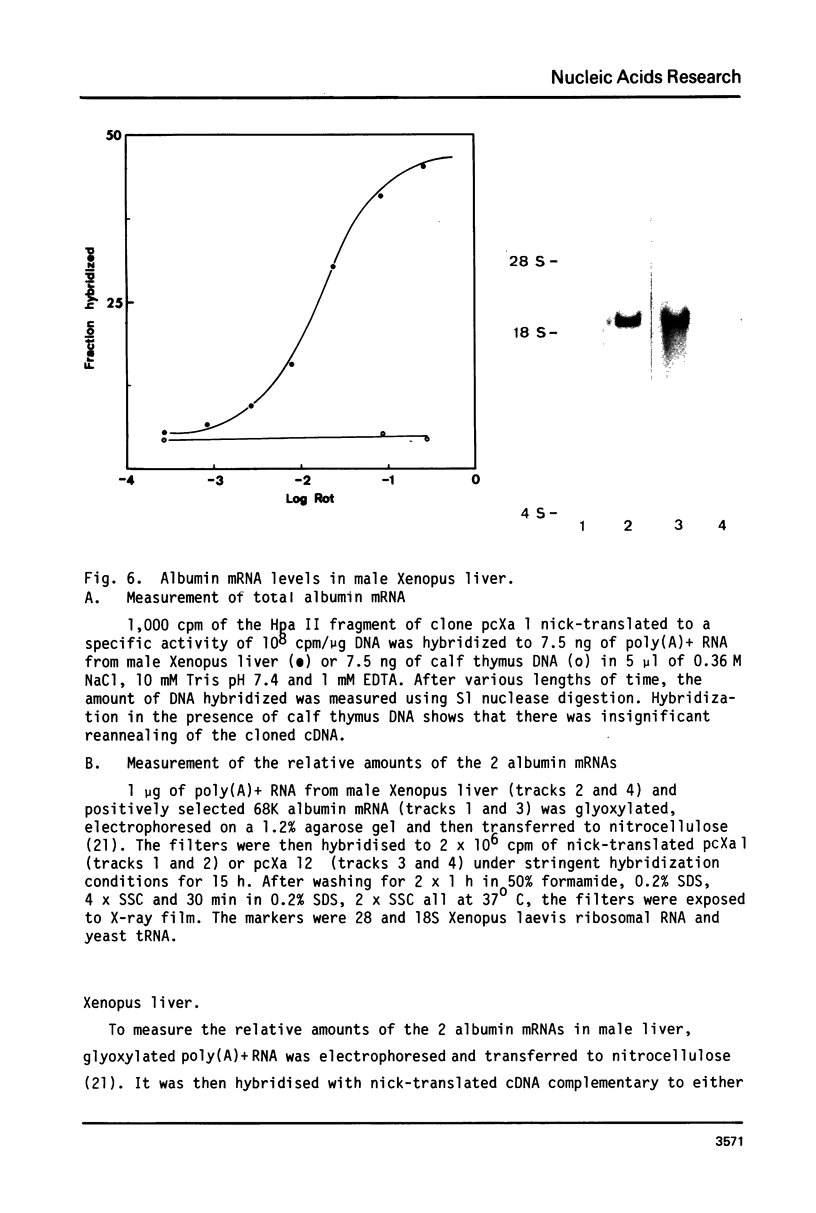
cDNA clones containing sequences complementary to Xenopus laevis albumin mRNA have been identified in a collection of cDNA clones made from poly(A)+ RNA prepared from male Xenopus laevis liver. Although all the albumin cDNA clones crosshybridise, restriction enzyme and heteroduplex analysis show that there are 2 closely related albumin mRNA sequences. The 2 albumin mRNAs are only mismatched by 8% but could be isolated by positive selection using stringent hybridization conditions. Oocytes injected with the 2 purified mRNAs, secreted either the 68,000 or 74,000 dalton albumin into the culture medium showing that the 2 albumins of X. laevis serum are encoded in the 2 closely related mRNAs. Measurements of the abundance of albumin mRNA show that the 2 albumin mRNAs together account for about 9% of total poly(A)+ RNA in male Xenopus laevis liver but the mRNA coding for the 74,000 dalton mRNA is about twice as abundant as that coding for the 68,000 dalton mRNA.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTH L. G., BARTH L. J. Differentiation of cells of the Rana pipiens gastrula in unconditioned medium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1959 Jun;7:210–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Christmann J. L., Deeley R. G. Cloning of a double-stranded cDNA that codes for a portion of chicken preproalbumin. A general method for isolating a specific DNA sequence from partially purified mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8629–8639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Wood D., Simons J. P., Kay R. M., Williams J. G. Linkage of adult alpha- and beta-globin genes in X. laevis and gene duplication by tetraploidization. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D., McConaughy B. L., McCarthy B. J. Rate of fixation of nucleotide substitutions in evolution. Nature. 1969 Oct 11;224(5215):149–154. doi: 10.1038/224149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D., Colman A., Mohun T., Morser J., Champion J., Kourides I., Craig R., Higgins S., James T. C., Applebaum S. W. The Xenopus oocyte as a surrogate secretory system. The specificity of protein export. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledford B. E., Frieden E. Albumin synthesis during induced and spontaneous metamorphosis in the bullfrog Rana catesbeiana. Dev Biol. 1973 Jan;30(1):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U. Comparison of cytoplasmic and nuclear poly(A)-containing RNA sequences in Xenopus liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):417–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Wahli W., Weber R. Quantitation of vitellogenin messenger RNA in the liver of male Xenopus toads during primary and secondary stimulation by estrogen. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Wu J. R., Sala-Trepat J. M., Wallace R. B., Reyes A. A., Bonner J. The rat serum albumin gene: analysis of cloned sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Williams J. G. Quantitative analysis of specific labelled RNA'S using DNA covalently linked to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):195–203. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman J. S., McCarthy B. J. The relationship between mismatched base pairs and the thermal stability of DNA duplexes. I. Effects of depurination and chain scission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Rochefort H. A secreted glycoprotein induced by estrogen in human breast cancer cell lines. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]