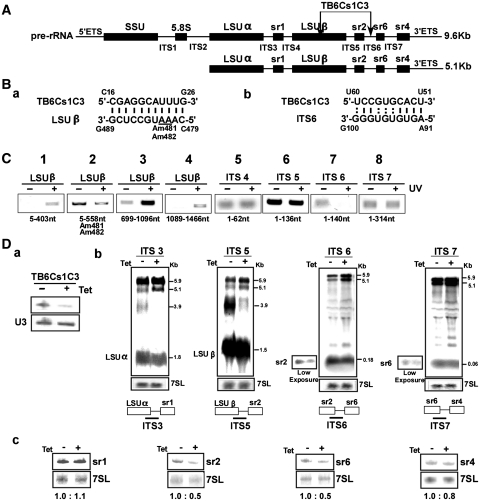
Figure 6.
The role of TB6Cs1C3 in rRNA processing. (A) Schematic representation of the pre-rRNA. The coding sequences are in black. The identity of the intergenic regions is given, and the position of the interaction of TB6Cs1C3 with the target are indicated. (Ba- and b-), Proposed interaction domain between the snoRNA and its targets. (C) ‘RNA walk’ to validate the interaction of TB6Cs1C3 with its target. RT–PCR along the pre-mRNA. cDNA was prepared from the affinity selected RNA of untreated cells or after treatment with AMT and UV cross-linking. The cDNA was subjected to PCR using the set of primers indicated, and the PCR products were separated on a 1% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. (D) Monitoring the accumulation of rRNA precursors in TB6Cs1C3 silenced cells. (D-a) Silencing of TB6Cs1C3. a-RNA was prepared from uninduced cells and cells 3 days after silencing, and subjected to primer extension with the snoRNA specific primer and U3 primer. (D-b) Northern analysis. Total RNA was extracted from cells carrying the TB6Cs1C3 RNAi construct without induction (−Tet), and after 3 days of induction (+Tet) and separated on a 1.2% agarose gel containing 2.2 M formaldehyde. The RNA was blotted and hybridized with the indicated probes. The 7SL RNA probe was used to control the amount of RNA of each sample. The marker sizes are indicated in kilobase pairs. (D-c) Monitoring defects in srRNA processing. Total RNA was extracted from cells carrying the TB6Cs1C3 RNAi construct without induction (−Tet), and after 3 days of induction (+Tet) and separated on a 10% acrylamide denaturing gel and subjected to northern analysis with srRNA probes. The 7SL RNA probe was used to control the amount of RNA in each sample.