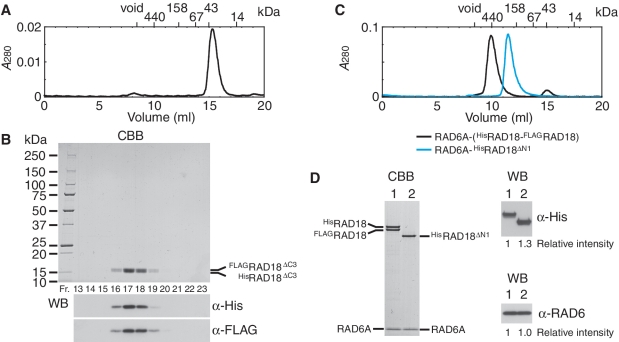
Figure 6.
Analysis of RING domain for dimerization of RAD18. (A) Elution profile of HisRAD18ΔC2–FLAGRAD18ΔC2 complexes from a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. The size markers, ferritin (440 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), albumin (67 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa) and ribonuclease A (14 kDa) were eluted in 10.09, 12.26, 13.74, 14.98 and 17.56 ml, respectively. The complex was eluted in 15.35 ml, estimated the apparent molecular mass of the complex to be 37 kDa from a standard curve of the marker proteins. (B) Analysis of fractions eluted from a Superdex 200 gel filtration column (A). Fractions between 13 and 18.5 ml were analyzed by SDS–PAGE followed by staining with CBB and western blotting probed with the indicated antibodies. HisRAD18ΔC2 (15.1 kDa) migrated slightly faster than FLAGRAD18ΔC2 (14.2 kDa). (C) Elution profile of RAD6A–(HisRAD18–FLAGRAD18) and RAD6A–HisRAD18ΔN1 complexes from a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. Respective complexes were eluted in 9.77 and 11.45 ml, corresponding to 490 and 220 kDa of the apparent molecular masses, and 62 and 52 Å of Stokes' radius, estimated from a standard curve of the marker proteins. (D) Peak fractions of gel filtration chromatography (C) were analyzed by SDS–PAGE followed by CBB staining and western blotting probed with the indicated antibodies. Relative chemiluminescence signals detected with a CCD camera are shown. Lane 1, RAD6A–(HisRAD18–FLAGRAD18) (3.7 pmol as a trimer); lane 2, RAD6A–HisRAD18ΔN1 (3.7 pmol as a dimer).