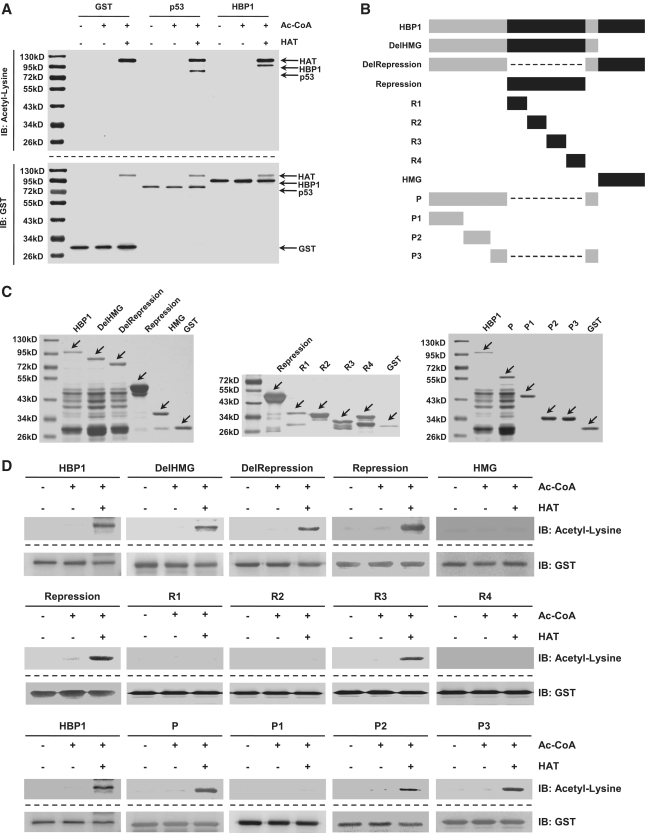
Figure 6.
Wild-type HBP1 and mutants were acetylated by HAT of p300/CBP in vitro. (A) HBP1 was acetylated by HAT in vitro. At the top, purified GST-tagged HBP1 protein was incubated with HAT in the presence of Ac-CoA. The reaction products were separated by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the acetyl-lysine antibody. At the bottom, the same nitrocellulose membrane as used in the in vitro acetylation assay described above was stripped and immunoblotted with anti-GST antibody. GST and GST-tagged p53 proteins were used for negative and positive controls, respectively. (B) Schematic diagram of wild-type HBP1 and associated mutants. (C) Expression of wild-type HBP1 and associated mutants proteins in E. coli. GST-tagged proteins were immunoprecipited with GST, then ran on SDS–PAGE and stained with silver. (D) HBP1 and some mutants (Repression domain, P domain) were acetylated by HAT in vitro. GST-tagged proteins from experiments shown in (B) were incubated with Ac-CoA and HAT in 30°C for 4 h. The reaction products were separated by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the acetyl-lysine antibody. GST was as loading control.