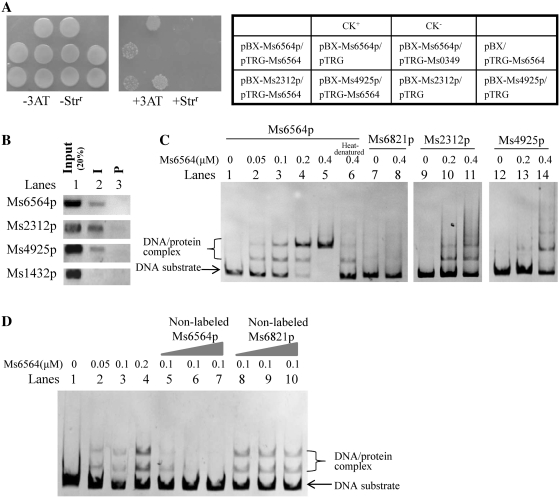
Figure 1.
Interaction of Ms6564 with the promoter regions of RecA-dependent and RecA-independent DNA repair genes and its own promoter region. (A) Bacterial one-hybrid assays. The promoter of the Ms2312, Ms4925 and Ms6564 genes was cloned into pBXcmT, and Ms6564 was cloned into pTRG vectors. A pair of pBXcmT/pTRG plasmids was co-transformed into the reporter strain and then its growth was tested together with the self-activation controls on a selective medium containing 3-AT, Kanr, Strr and Chlr as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. An outline of the plates is shown in the right panel. Each unit represents the corresponding co-transformant in the plates. (B) ChIP assays. ChIP using preimmune (P) or immune sera (I) raised against Ms6564. Exponentially growing M. smegmatis cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde. Crosslinked cells were resuspended and sonicated on ice. A 100 µl sample of the extract was saved as the input fraction, with the remaining 900 µl incubated with 10 µl of antibodies against Ms6564 at 4°C. The complexes were immunoprecipitated with 20 µl 50% protein A-agarose. The immunocomplex was recovered by centrifugation and resuspended in 100 µl TE. Crosslinking was reversed for 6 h at 65°C. The DNA samples of the input and ChIP were purified and resuspended in 50 µl TE. Then the DNA recovered from the immunoprecipitates was amplified with primers specific for DNA repair genes or to an unrelated mycobacterial promoter of Ms1432 used as a negative control. (C) EMSA assays. 32P-labeled Ms6564p (lanes 1–5), Ms2312p (lanes 9–11), Ms4925p (lanes 12–14) or Ms6821p (a non-specific DNA, lanes 7 and 8) DNA substrates were co-incubated with various amounts of Ms6564 protein. The heat-denatured Ms6564 was used as negative control (lane 6). The free DNA substrate and DNA–protein complex are indicated. (D) EMSA assays for the specific binding of Ms6564 with the DNA substrate. Unlabeled cold Ms6564 or unspecific Ms6821 promoter DNA substrates were used to compete with the [γ-32P] ATP labeled Ms6564 promoter DNA. Cold Ms6564 promoter DNA, but not Ms6821 promoter DNA, could competitively inhibit the binding of Ms6564 to the labeled Ms6564 promoter DNA substrate.