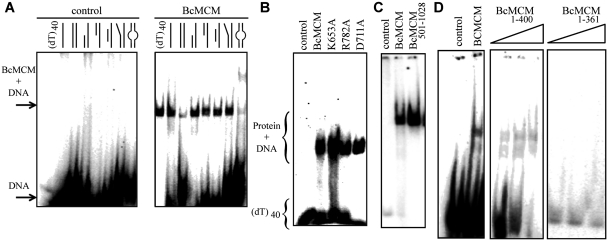
Figure 2.
The BcMCM protein binds DNA. (A) Native EMSA assays using different DNA structures. Sketches of the different DNA probes used in the assay are indicated above each lane. The assay without BcMCM was used as negative control. The 40-nt lane corresponds to a 40-nt poly-dT, (dT)40, a probe to discard binding to DNA secondary structures, and was used in subsequent assays. The sequences of the probes are described in Supplementary Table SII. Arrows and brackets indicate positions of the shifted protein–DNA complex and free DNA. All the assays were carried out using 1 µM of protein, unless otherwise indicated, and 1 nM of DNA. (B) Mutations in the ATPase site do not affect DNA binding. (C) The helicase domain BcMCM501–1028 is able to bind DNA. (D) The canonical primase domain BcMCM1–361 (1–3 µM) does not bind DNA. However, BcMCM1–400 (1–3 µM) shows weak binding compared to the wild-type protein.