Figure 5.
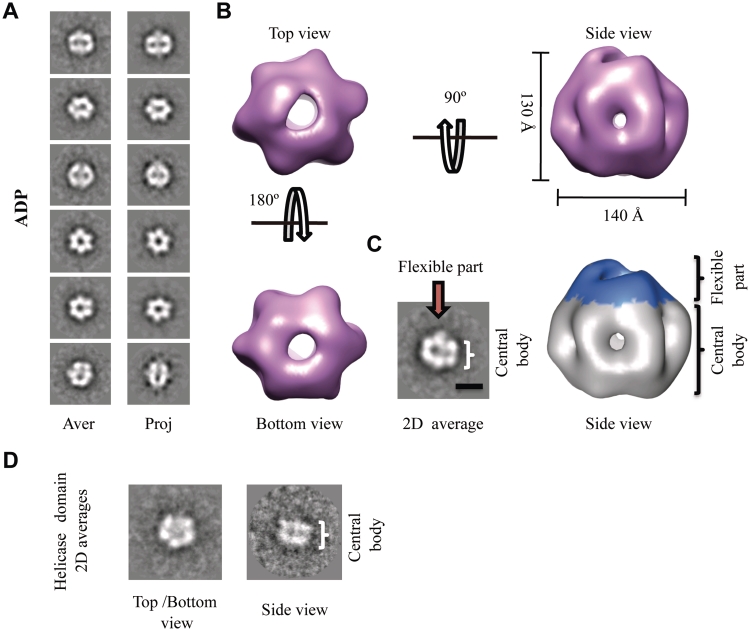
3D reconstruction of the BcMCM–ADP hexamer. (A) Gallery of selected reference-free 2D averages (left panel) compared to the corresponding reprojections of the final structure (right panel). (B) Surface representation of the 3D reconstruction of BcMCM–ADP hexamer filtered to 36 Å shown in different orientations. The protein monomers assemble into a single hexameric ring around a large central cavity displaying differences between the top and the bottom views. The overall dimensions of the complex are depicted in the figure. (C) The BcMCM–ADP hexamer (right panel) consists of a central body indicated (coloured in grey) and a flexible apical part (coloured in blue). In the 2D average side view (left panel) the central body and the flexible part are indicated with a bracket and an arrow respectively. A 100-Å bar is provided as a reference. (D) A typical reference-free 2D class averages of the BcMCM501–1028 helicase domain resembles the 2D averages of the BcMCM complex.