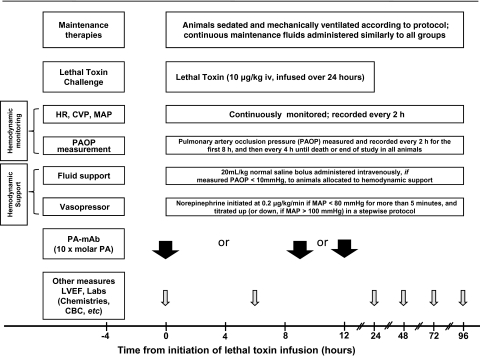
Figure 1.
Timeline of experimental interventions, measurements, and treatments. As outlined in “Methods,” at the initiation of 24-h lethal toxin infusions, animals were randomized to receive hemodynamic support alone, protective antigen–directed monoclonal antibody (PA-mAb) at the time of or 9 or 12 h after starting toxin infusion, hemodynamic support combined with PA-mAb (administered at 0, 9, or 12 h), or no treatment (control). Hemodynamic support included a single bolus of 20 mL/kg of normal saline if the pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP, checked every 2 h for the first 8 h and every 4 h thereafter) was <10 mmHg. Also, if at any time the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) decreased to <80 mmHg for >5 min, a norepinephrine (NE) infusion was initiated at 0.2 μg/kg/min and, if necessary, increased in a stepwise fashion every 5 min to 0.6, 1, or a maximum of 2 μg/kg/min. NE was titrated down in a stepwise fashion if MAP was >100 mmHg for >5 min. Abbreviations: ABG, arterial blood gas; CBC, complete blood count; CVP, central venous pressure; HR, heart rate; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction (measured with echocardiography).