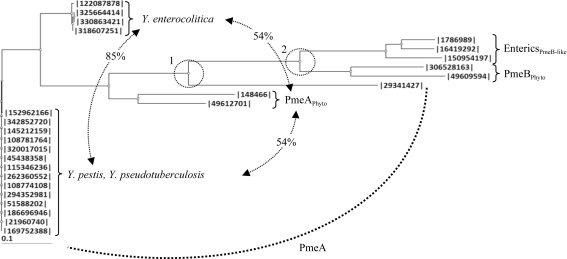
Figure 3.
Phylogram of CE8 enzymes from Yersinia and bacterial phytopathogens and enteropathogens. Neighboring-joining phylogram of CE8s from Y. pestis (342852720, A1122; 145212159, Pestoides F; 108781764, Antiqua; 320017015, biovar Mediaevalis str. Harbin 35; 5438358, biovar Microtus str. 91001; 115346236, CO92; 262360552, D106004; 21960740, KIM 10; 108774108, Nepal516; 294352981, Z176003), Y. pseudotuberculosis (152962166, IP_31758; 51588202, IP_32953; 186696946, PB1/+; 169752388, YPIII) and Y. enterocolitica [122087878, subsp. enterocolitica 8081; 325664414, subsp. palearctica 105.5R(r); 318607251, subsp. palearctica Y11; 330863421, W22703] strains with (1) PmeA from B. thetaiotaomicron (29341427) and the phytopathogens D. dadantii 3937 (148466) and Pectobacterium atrosepticum SCRI1043 (49612701), (2) PmeB from D. dadantii 3937 (306528163) and P. atrosepticum SCRI1043 (49609594) and (3) PmeB-like enzymes from the enteropathogens K. pneumonia subsp. pneumonia MGH78578 (150954197), S. enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (16419292) and E. coli str. K-12 substr. MG1655 (1786989). The relatedness (represented as percentage identity) between the Y. enterocolitica, PmeAPhyto and Y. pestis/Y. psudotuberculosis subclades are labelled. Two significant divergences separating the Yersinia enzymes from the other PMEs and the PmeAs from the PmeBs are indicated by dashed circles and labelled.