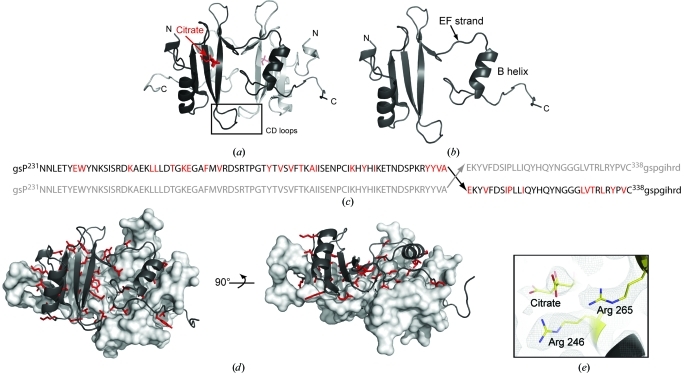
Figure 2.
(a) Structure of the Itk SH2 domain-swapped dimer. The monomer units are colored black and gray, citrate is shown in red and the CD loops of each monomer (containing Pro287) are boxed and labeled. (b) The asymmetric unit of the SH2-domain crystal structure is a monomer with an extended EF strand and dislocated B helix. (c) Primary sequence of Itk SH2 showing the site of swapping in the dimer structure (Ala307–Glu308). Upper case indicates the sequence of Itk SH2 and lower case indicates the vector-derived sequence. The amino acids colored red indicate those for which side-chain interactions across the dimer interface are observed. (d) Two views of Itk SH2 dimer interface observed in the crystal structure. The surface of one monomer is depicted (gray) and the opposing monomer is represented using ribbons to illustrate the dimer interface. The residues that are oriented toward the opposing monomer in the dimer structure are shown as red sticks [the same as those highlighted in (c)]. (e) Citrate in the phosphotyrosine (pY) binding pocket in the Itk SH2 crystal structure. Arg246 and Arg265 (conserved pY binding residues) and the bound citrate molecule are shown as a 2F o − F c electron-density map contoured at 1σ.