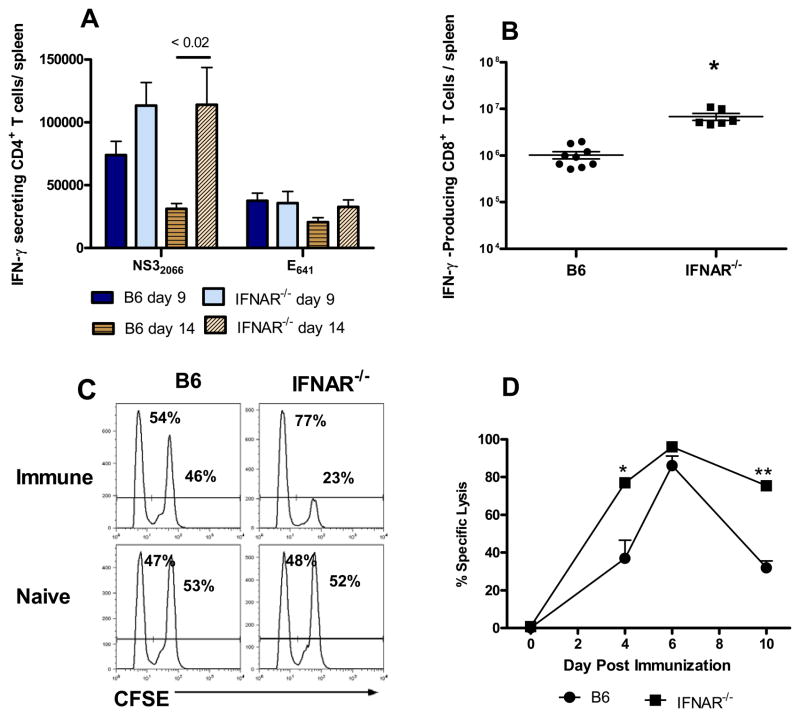
Fig. 5.
Type I IFN receptor signaling is not required for the intrinsic adjuvanting of T cell responses against RepliVAX WN. (A) CD4+ T cell response. B6 or IFNAR−/− mice were immunized with 106 IU RepliVAX WN and the number of IFN-γ-secreting cells specific for the NS32066 or E641 CD4+ T cell epitopes were quantified by ELISPOT on days 9 and 14 as described in Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as the number of IFN-γ-secreting cells/spleen (mean ± SEM) and are compiled from 2 separate experiments (n = 10–12 mice/group). (B) CD8+ T cell responses to the NS4B2488 epitope were quantified by detection of intracellular IFN-γ by flow cytometry on day 6 as described in Methods. Results are expressed as the number of IFN-γ secreting cells/spleen (mean ± SEM) and are compiled from 2 separate experiments (n = 6–9 mice/group). (C) Representative histograms of CFSE-labeled target cells in spleens of naïve and RepliVAX WN-immunized B6 and IFNAR−/− mice 4 days after immunization. Numbers in each histogram represent the % No-peptide targets (CFSElow) and % NS4B2488 peptide-pulsed targets (CFSEhi) for an individual animal. (D) Cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocyte activity from B6 and IFNAR−/− mice after RepliVAX WN immunization. The percentages of CFSElow and CFSEhi targets derived as shown in Fig. 5C, were used to calculate a % specific lysis as described previously [19]. Results are expressed as the % specific lysis (mean ± SEM) from 5 mice/group for NS4B2488-coated targets (* p < 0.005, ** p < 0.0001 compared to RepliVAX WN-immunized B6 mice). Naïve mice routinely exhibited < 2% specific lysis.