Figure 7. ACD2 acts cell autonomously in mosaic plants.
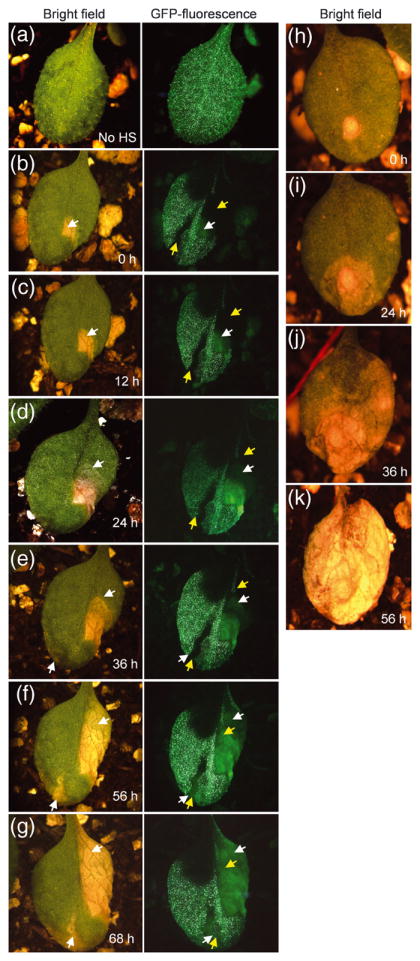
Homozygous acd2 plants carrying both heat shock inducible CRE recombinase and LOX recombination sites flanking genes encoding ACD2 and nuclear-GFP were used to study cell death patterns. The initiation and spreading of cell death lesions were followed in single leaves over 10-12 h time intervals. This experiment was done three times with similar results. Twenty-six leaves were analyzed. Lesions in panels “b” and “h” were arbitrarily assigned time 0 h.
(a) Non heat-shocked (No HS) control plant showed GFP throughout the leaf.
(b) Leaves showing GFP− sectors after heat-shock treatment. The yellow colored arrow marks the GFP− sector area. The white arrow marks the initiation of cell death. Note the cell death areas under GFP channel gave autofluorescence that was lighter in color compared to GFP and also lacked the nuclear-localization seen with GFP fluorescence.
(c) and (d) Note the spreading of cell death lesions (follow the spreading of the lesion in the bright field image and the autofluorescence area in the GFP− sectors). However, the spreading of the lesion was contained in the area with GFP.
(e) A second lesion started in the other GFP− sector (follow the white arrow in bright field as well as GFP channel).
(f) and (g) Spreading of the new lesion in the GFP− sector (f). (g) Note that the leaf is alive after 68 h of light exposure.
(h - k) Initiation and spreading of cell death in acd2. Note that the cell death spreads continuously from its starting point to consume the whole leaf. Although panel k shows a completely dead leaf at 56 h, this leaf was dead by 48 h.
