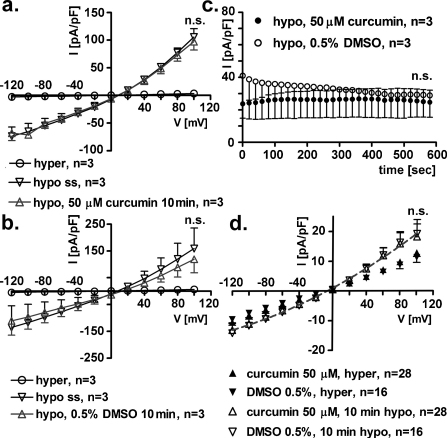
Fig. 2.
Short-term exposure to extracellular or intracellular 50 μM curcumin does not affect IClswell. IClswell was activated in human renal cells (HEK293 Phoenix) by hypotonic shock and measured by the patch clamp technique in whole cell configuration. (a) Current density-to-voltage relations measured in extracellular hypertonic solution (hyper), at the maximal activation of the current in extracellular hypotonic solution (or steady state (hypo ss)), and after a 10 min exposure to an extracellular hypotonic solution containing 50 μM curcumin. (b) Current density-to-voltage relations measured in extracellular hypertonic solution (hyper), at the maximal activation of the current in extracellular hypotonic solution (or steady state (hypo ss)) and after a 10 min exposure to an extracellular hypotonic solution containing 0.5% DMSO as the vehicle. The current is not affected by a 10 min exposure to curcumin or DMSO (paired Student's t-test). (c) Current density-to-time graph showing the current in extracellular hypotonic solution containing 50 μM curcumin or 0.5% DMSO; the current is not affected by a 10 min exposure to curcumin or DMSO (paired Student's t-test). (d) Current density-to-voltage relation measured in extracellular hypertonic solution (hyper) and after a 10 min exposure to extracellular hypotonic solution (10 min hypo) in cells where 50 μM curcumin or 0.5% DMSO was added to the pipette filling (intracellular) solution. Data were fitted with second order polynomials (dotted line), following application of the extra-sum of squares F test and showed no effect of intracellular, short-term incubation with 50 μM curcumin.