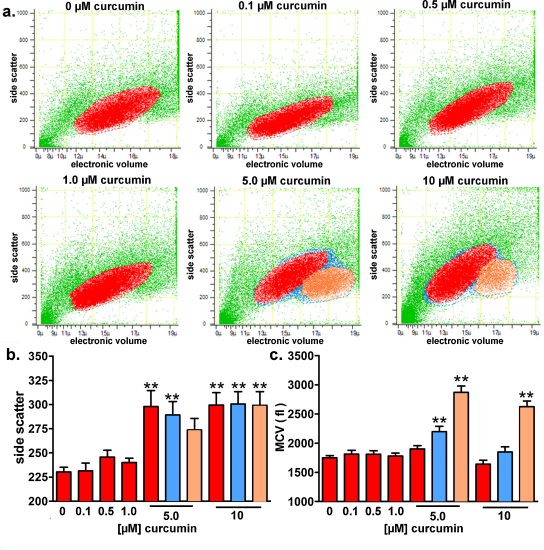
Fig. 6.
Long-term exposure to curcumin induces apoptosis in HEK293 Phoenix cells and the appearance of a new sub-population of cells with a nearly doubled volume. The effect of long-term exposure (19 h in a complete medium) to 0.1–10 μM curcumin on the side scatter and cell volume was investigated on HEK293 Phoenix cells by flow cytometry. Control cells were incubated with 0.05% DMSO. (a) Original dot plots of the side scatter (expressed in arbitrary units) versus cell diameter (μm; electronic cell volume); red, orange and blue colors indicate the main population of cell with normal volume, the new cell population with an increased volume and the sum of the two populations, respectively. Bar diagrams of (b) the mean side scatter and (c) the mean cell volume (MCV, fl); red, orange and blue bars refer to the main population of cells with normal volume, the new cell population with an increased volume and the sum of the two populations, respectively. **p < 0.01, one way ANOVA with Dunnet's post-test. Data were collected from 6 independent experiments.