Fig. 1.
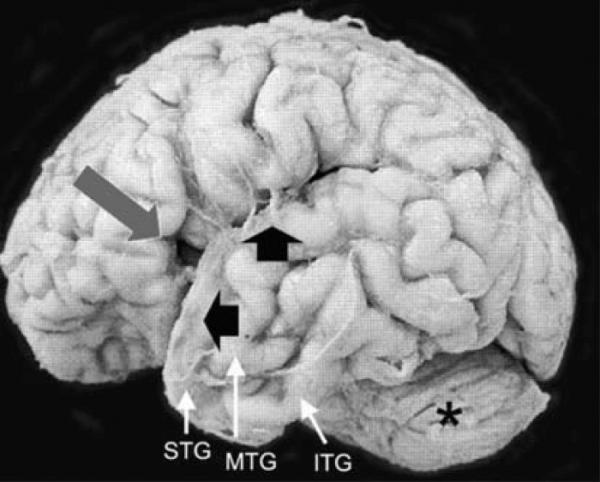
The external appearance of the brain of our neonatal case with Haddad syndrome was remarkable for a developmentally inappropriate opercula (long arrow) and small size of the superior temporal gyrus (STG) (short arrow). The middle temporal gyrus (MTG) appears split posteriorly; the inferior temporal gyrus (ITG) is unremarkable. The cerebellum (asterisk) is of appropriate size relative to the cerebrum
