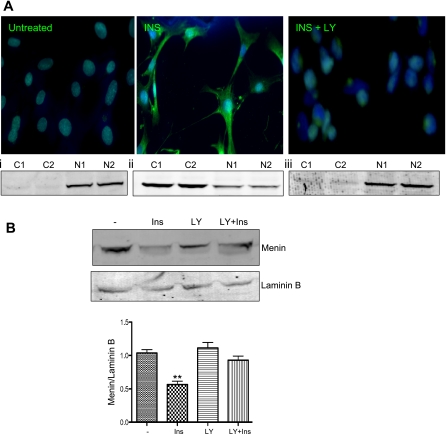
Fig. 3.
Ins shuttles menin from the nucleus into the cytoplasm via Akt signaling. A: flourescent images of menin in HepG2 cells after 24-h exposure to 100 nM insulin show cytoplasmic localization inhibited by LY-294002 (INS + LY). A, i–iii: menin expression in cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractionation from untreated HepG2 cells (i), HepG2 cells treated with 100 nM insulin (ii), and HepG2 pretreated with LY-294002 for 1 h prior to insulin treatment (iii). B: Western blotting with 30 of μg nuclear lysates from HepG2 cells exposed to 100 nM Ins or 10 μM LY 1 h prior to Ins (LY + Ins). Lamin B used for control of nuclear lysates. Graph shows densitometry of near infrared band intensity from 3 experiments. **P = 0.0014.