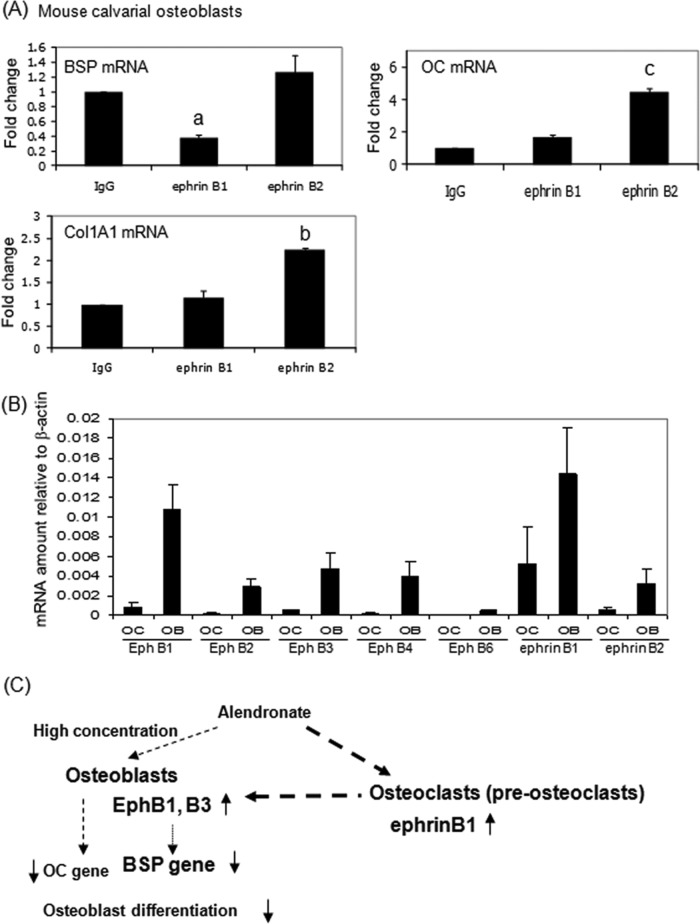
Figure 4.
Ephrin B1 inhibits bone sialoprotein (BSP) gene expression in vitro. (A) To stimulate forward or reverse signaling, ephrin B1-Fc, ephrin B2-Fc, or IgG-Fc fragments were clustered with anti-Fc antibody at 2 µg/mL for 1 hr, and then primary mouse osteoblasts were cultured with 50 µg/mL ascorbic acid and 10 mM β-glycerophosphate for 17 days on the clustered proteins. RNAs were measured by real-time RT-PCR. The relative levels of mRNAs were normalized to β-actin and then expressed as fold stimulation over control. Error bars represent ± SEM of 3 experiments. a, p < 0.001; b, p<0.003; and c, p < 0.02 compared with IgG. (B) Eph and ephrin expression in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The relative levels of mRNAs were normalized to β-actin. OB, primary mouse osteoblasts; OC, mouse osteoclasts derived from mouse bone marrow. (C) Schematic representation of osteoclast-osteoblast interactions and the effect of alendronate. Alendronate stimulated ephrinB1 gene expression in osteoclasts, which interacts with EphB1 or B3 receptors on osteoblasts to inhibit osteoblast function, especially BSP.