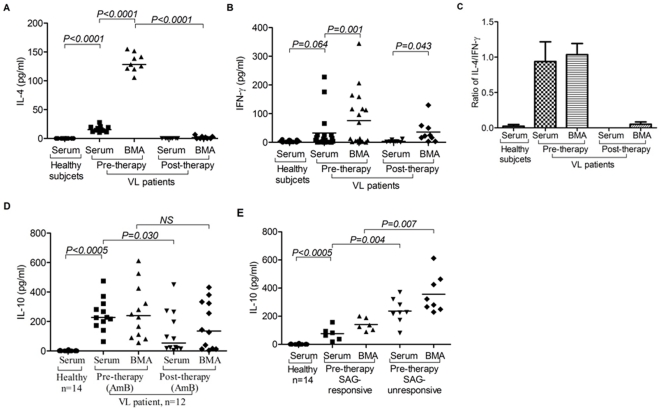
Figure 5. Dominance of soluble suppressive cytokine(s) at disease site (bone marrow, BM) of visceral leishmaniasis (VL) patients:
A) High Levels of IL-4 in BM among VL patients: Scatter plot shows increased level of IL-4 in serum of VL patients (n = 11) than that of HCs (n = 10; p = 0.0005, Unpaired t test). Its level was further increased in BMA of VL patients (n = 9; p = 0.0005, Paired t test). After successful therapy (post), the IL-4 declined to undetectable levels in serum (n = 8) and BMA (n = 9) of cured VL cases. B) Elevated levels of IFN-γ among VL patients: Scatter plot depicting higher levels of IFN-γ (pg/ml) in the serum of untreated VL patients (n = 21) than that of HCs (n = 17; p = 0.064, unpaired t test). Level of IFN-γ is further increased in BMA (n = 19) as compared to that of autologous serum (n = 21, p = 0.001, Paired t test). After successful therapy (post), levels of serum IFN-γ is reduced in cured cases (n = 8) below their level at 0 day (pre). However, its level in BMA of cured cases (n = 9) remained high even after therapy, even though reduced to some extent after successful treatment (p = 0.043, Paired t test). C) Ratio of IL-4 and IFN-γ shows dominance of IL-4 over IFN-γ in serum as well as BMA before therapy. Post therapy, IFN-γ dominates over IL-4 quantitatively. D) High levels of IL-10 in untreated patients and its persistence after successful therapy with AmB: Increased levels of IL-10 was observed in the serum as well as BMA of untreated VL patients (n = 12) as compared to serum of HCs (n = 14; p = 0.0005, Unpaired t test). After therapy with AmB, IL-10 levels are maintained at high level in BMA (n = 12). E) IL-10 in SAG responsive and unresponsive patients: Pre treatment levels of IL-10 in the serum and BMA of VL patients could segregate SAG unresponsive patients from the responsive group. IL-10 levels were significantly higher in serum (p = 0.004, Mann Whitney test) and BMA (p = 0.007, Mann Whitney test) of patients who did not respond to SAG therapy. Horizontal line in dot plot depicts median value.