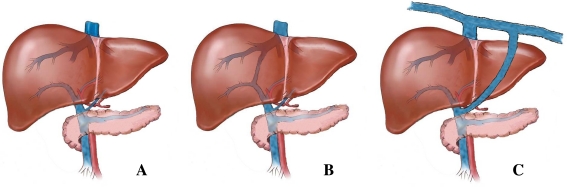
Fig. 1.
Overview of the anatomy of a normal liver and of livers with intra- and extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. a No connection of blood vessels in the liver is seen within a normal liver resulting in a blood flow through the hepatic sinusoids. b In case of PSS, blood bypasses the liver sinusoids and is therefore not subjected to hepatic metabolism. The intrahepatic shunt represents an abnormal connection of the portal vein with the systemic circulation, which is seen inside the liver. c In the case of an extrahepatic shunt, the aberrant connection is located outside the liver