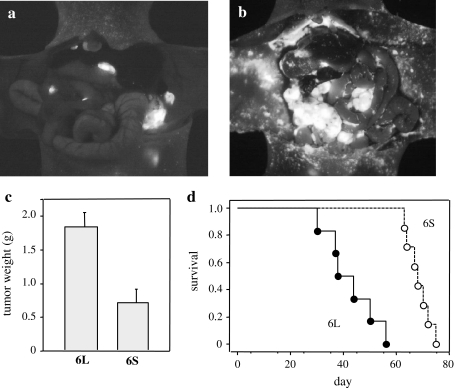
Fig. 2.
Increased metastasis and mortality in GCIY/6L-transplanted mice. a, b Recipient nude mice were i.p. injected with 4 × 106 GCIY/6L or GCIY/6S cells, and were subjected to laparotomy to visualize metastatic cells under UV light at 5 weeks after transplantation. The number of metastatic foci was definitively larger in GCIY/6L-transplanted mice (b) than in GCIY/6S-transplanted mice (a). c At this time point, peritoneal tumor masses were resected and weighed. GCIY/6L-derived tumor masses were significantly larger in weight than those of GCIY/6S. P < 0.005; n = 7 (GCIY/6L) and n = 5 (GCIY/6S). Bars represent standard errors (SE). d Overall survival of the recipient mice as depicted by the Kaplan-Meier method. Survival time was significantly shorter for GCIY/6L-transplanted mice (closed circles and a solid line) than for GCIY/6S-transplanted mice (open circles and a dotted lines). P < 0.0005; n = 6 (GCIY/6L) and n = 7 (GCIY/6S)