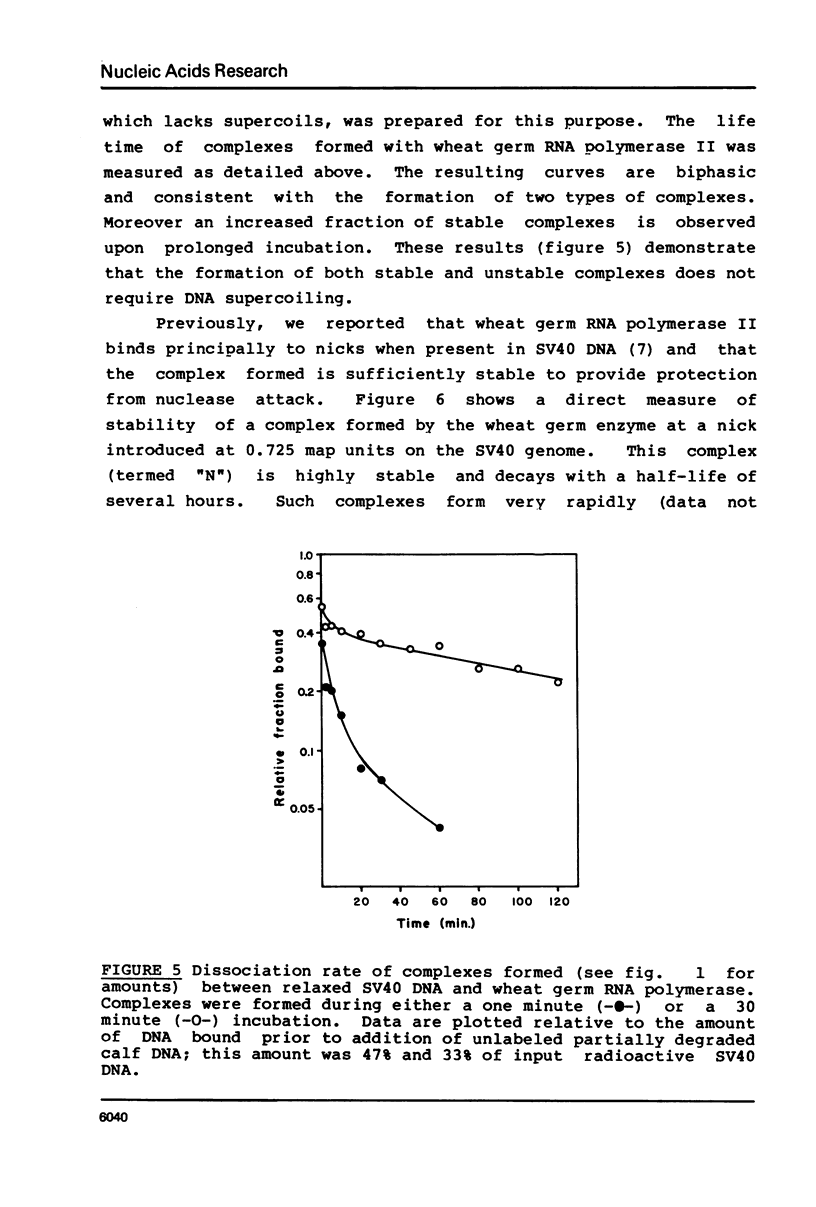
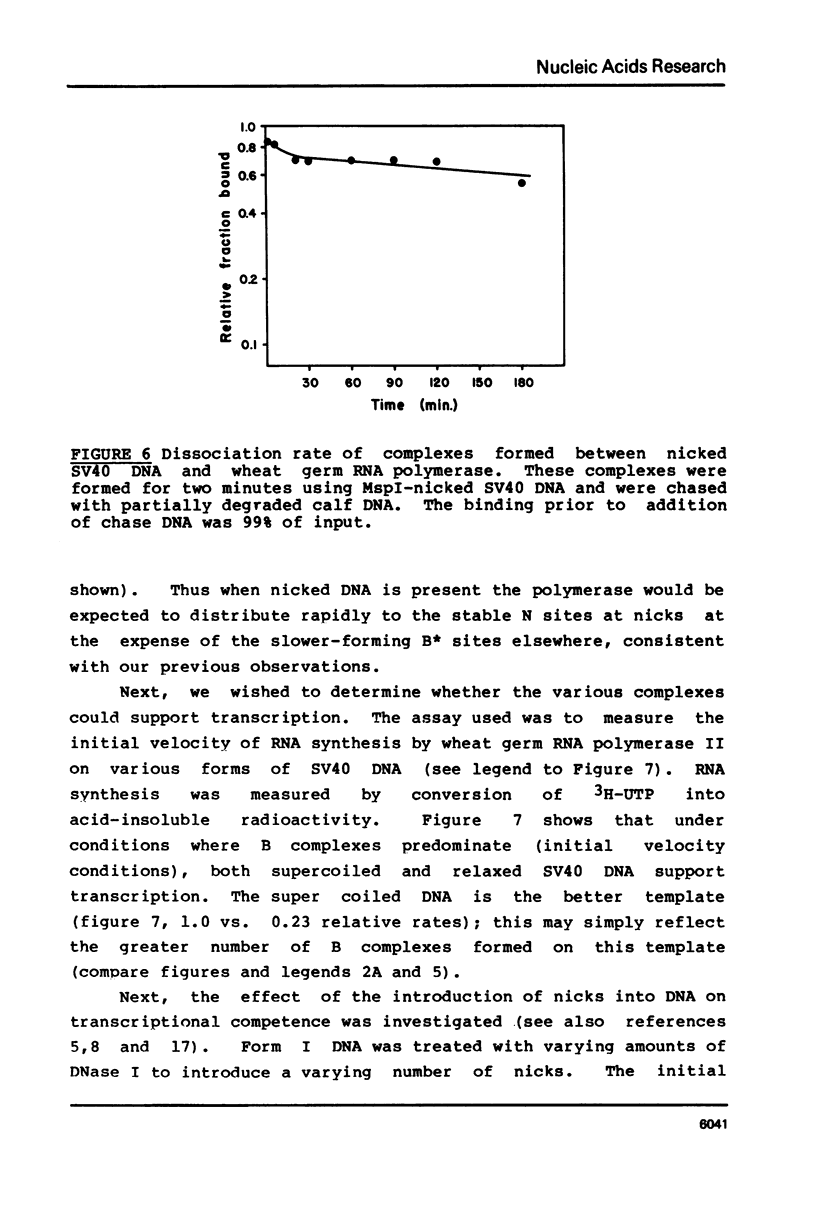
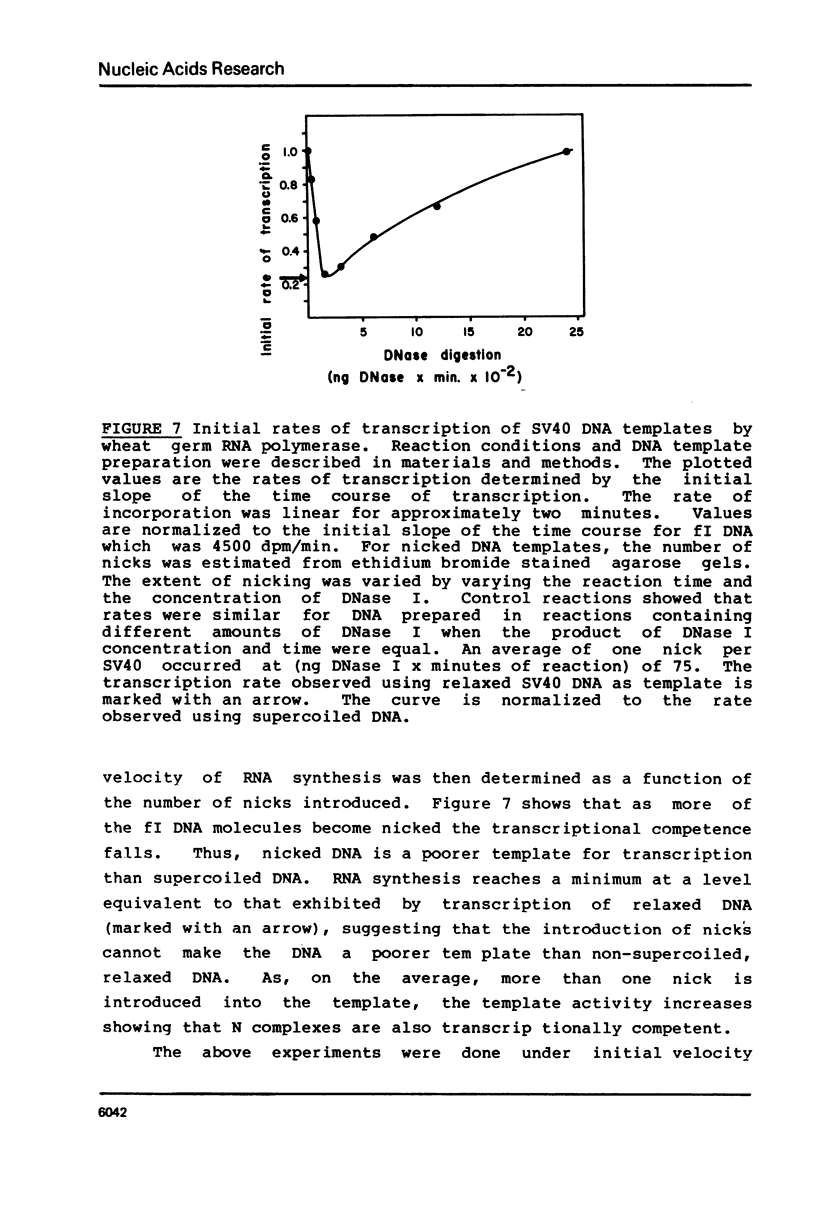
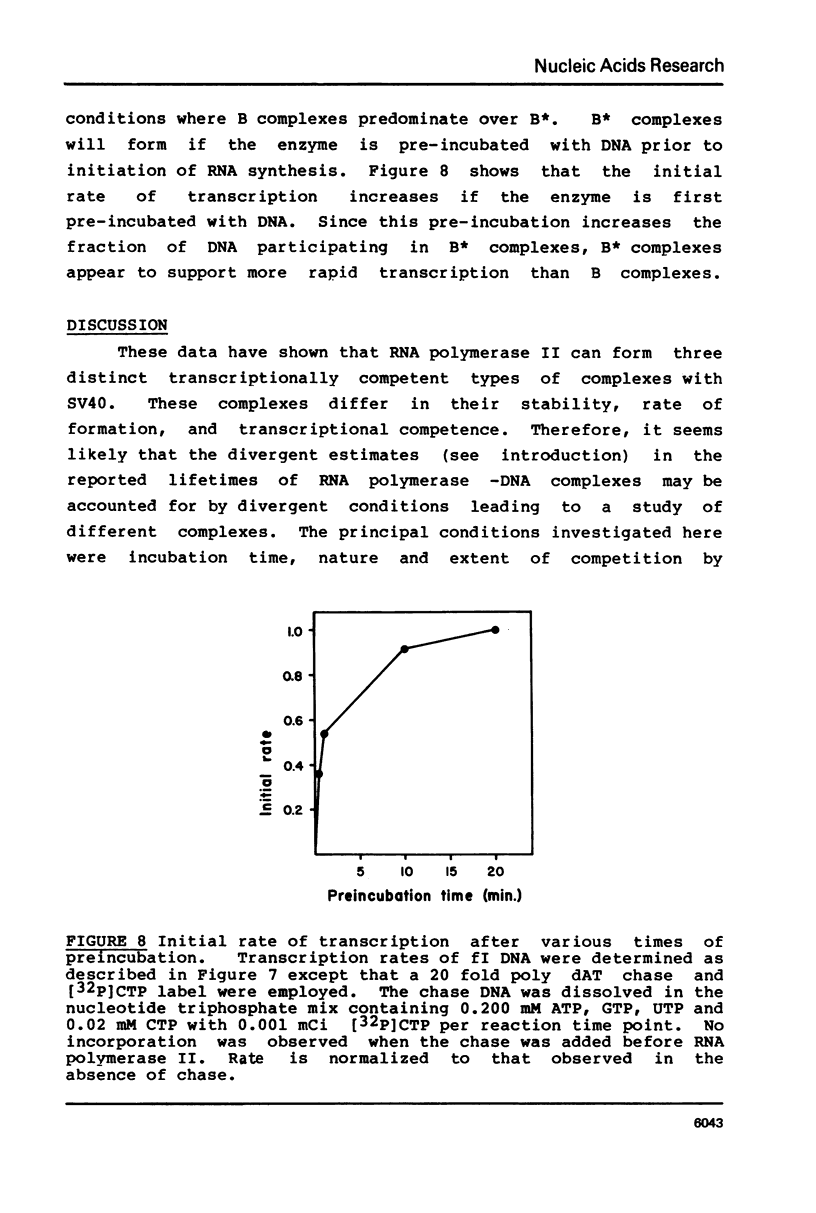
Abstract
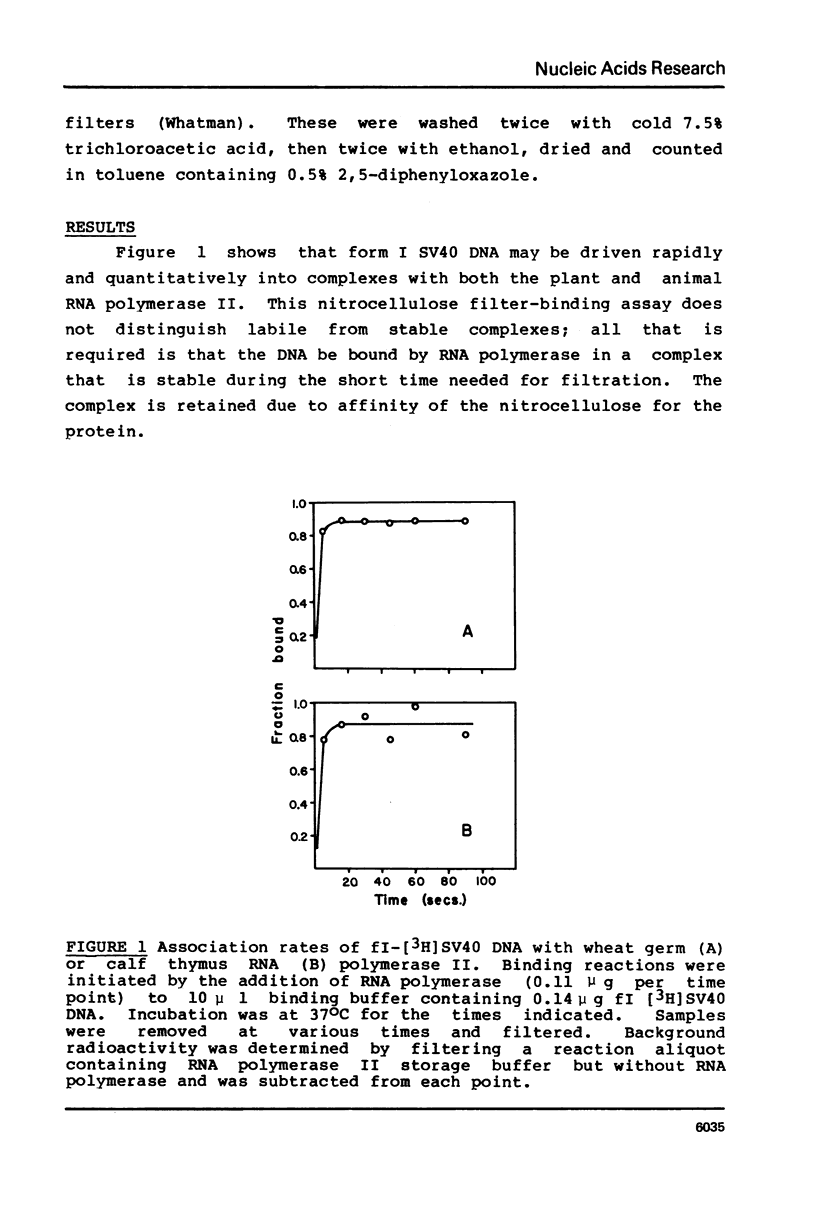
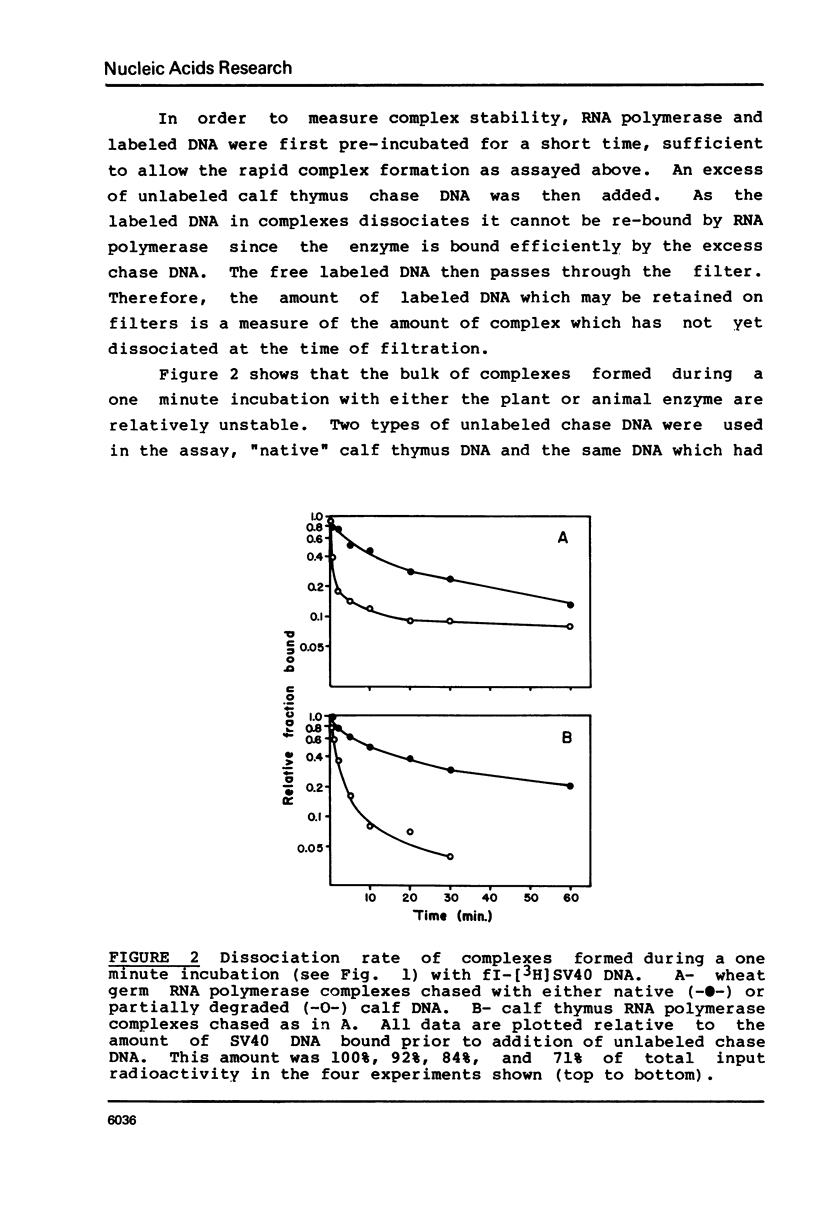
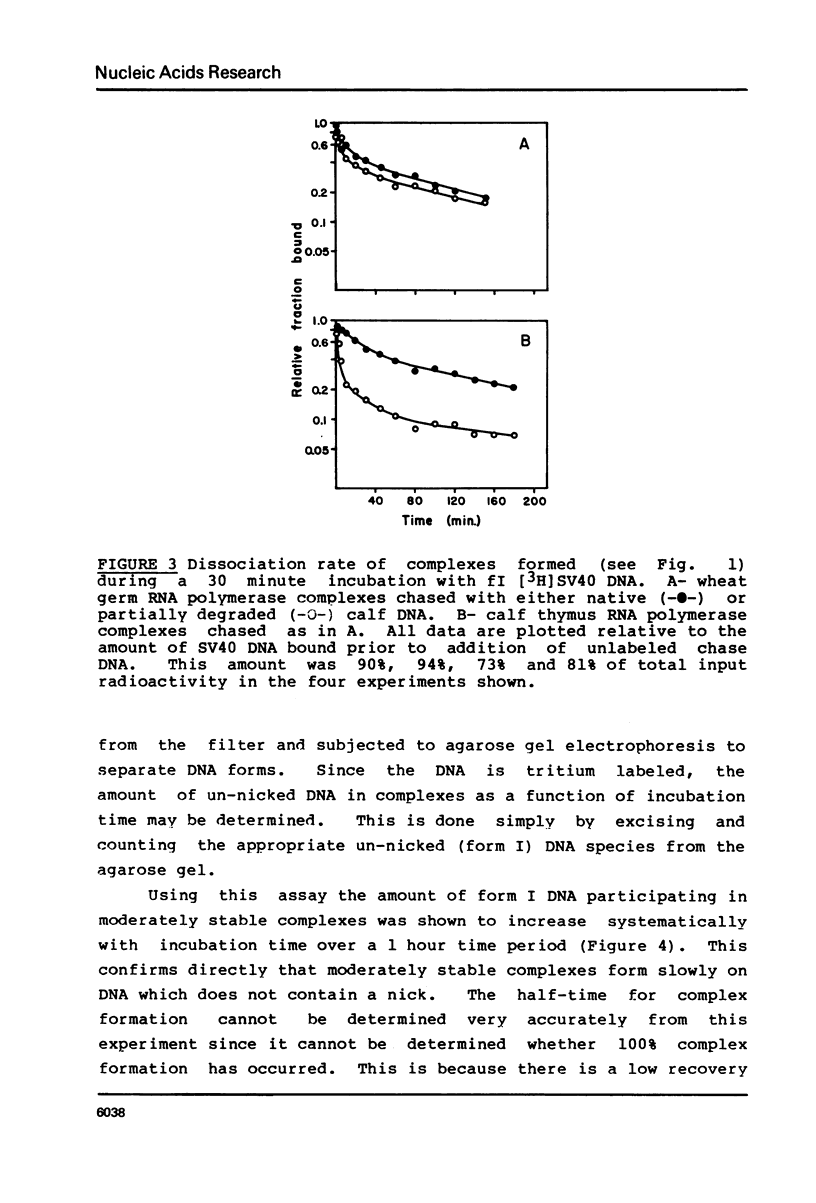
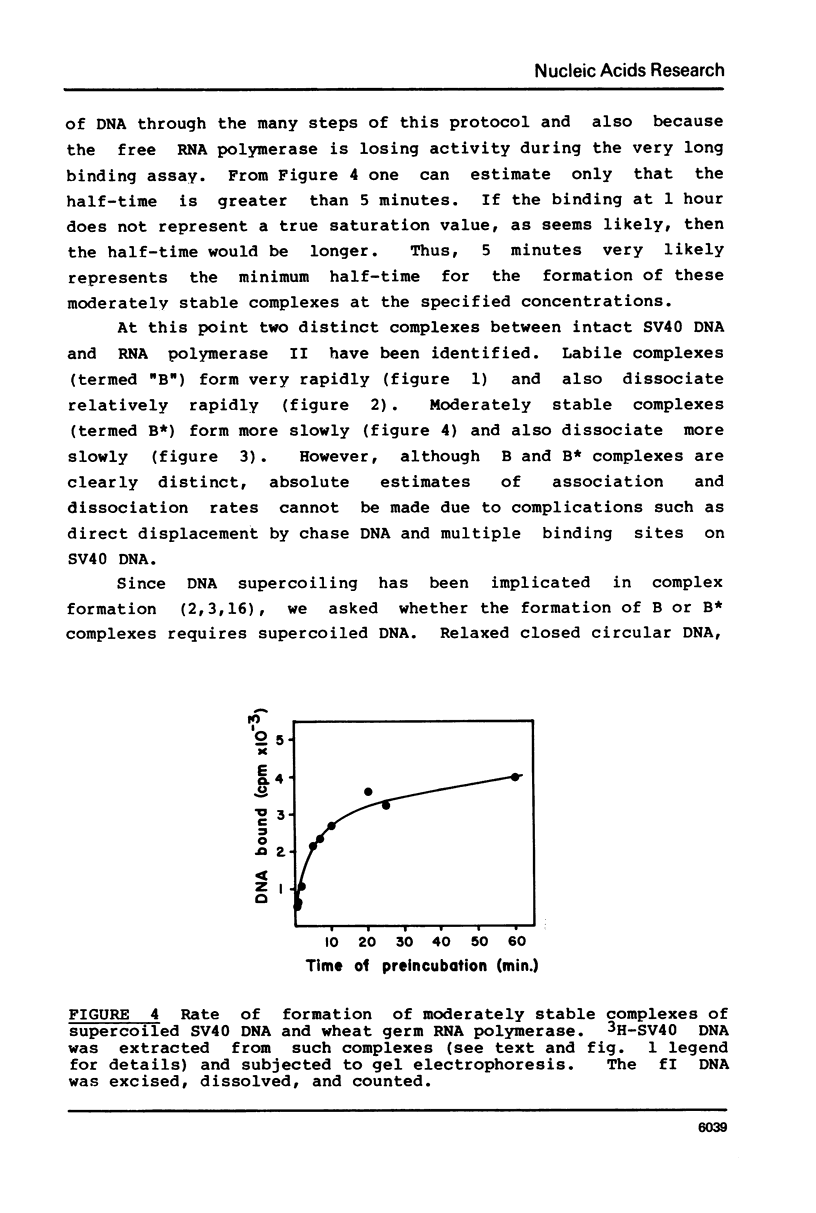
Various complexes formed between purified RNA polymerase II and simian virus 40 DNA have been characterized with respect to rates of formation, rates of dissociation, and initial velocity of RNA synthesis. Two different types of complexes can form on intact DNA templates. One of these is formed rapidly, but is quite labile; the other forms more slowly, but is moderately stable once formed. The introduction of a single strand break into DNA leads to rapid and stable complex formation, and thus is expected to create the favored binding site. The observed properties of these complexes provide a general framework for describing the interactions of RNA polymerase II at non-promoter DNA sites. This framework appears to be similar to that established for Escherichia coli RNA polymerase interactions, suggesting that the fundamental mode of non-promoter DNA binding is similar for the bacterial, plant, and mammalian enzymes.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitter G. A., Roeder R. G. Transcription of viral genes in chromatin from adenovirus 2 transformed cells by exogenous eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):433–452. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. W., Gralla J. Specific binding and protection of form II SV40 deoxyribonucleic acid by ribonucleic acid polymerase II from wheat germ. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1604–1612. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Burgess R. R. In vitro transcription by wheat germ ribonucleic acid polymerase II: effects of heparin and role of template integrity. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4581–4588. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. The role of sigma subunit in site selection. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):157–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle D. C., Ring J., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. 3. Tight binding of RNA polymerase holoenzyme to single-strand breaks in T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodo H. G., 3rd, Blatti S. P. Purification using polyethylenimine precipitation and low molecular weight subunit analyses of calf thymus and wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2334–2343. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Oudet P., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Studies on the binding of mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B to Simian virus 40 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):397–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrisak J. J., Burgess R. R. A new method for the large-scale purification of wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4639–4645. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Williams R. C., Chamberlin M. J. Electron microscopic studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. I. Characterization of the non-specific interactions of holoenzyme with a restriction fragment of bacteriophage T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T. R., Williams R. C., Chamberlin M. J. Electron microscopic studies of the binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase to DNA. II. Formation of multiple promoter-like complexes at non-promoter sites. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lescure B., Chestier A., Yaniv M. Transcription of polyoma virus DNA in vitro. II. Transcription of superhelical and linear polyoma DNA by RNA polymerase II. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. K., Burgess R. R. Transcription of simian virus 40 DNA by wheat germ RNA polymerase II. Priming of RNA synthesis by the 3'-hydroxyl of DNA at single strand nicks. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4928–4936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Houghton M. The interaction of RNA polymerase II from wheat with supercoiled and linear plasmid templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):507–523. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Reznikoff W. S. In vitro analysis of the Escherichia coli RNA polymerase interaction with wild-type and mutant lactose promoters. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):467–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Lescure B., Yaniv M. Comparative study of calf thymus and wheat germ RNA polymerase II: stability of initiation complexes and elongation rates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Nüsslein C., Schaller H. Interaction of RNA polymerase with promoters from bacteriophage fd. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):107–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman S., Surzycki S. J., DeLorbe W., Gussin G. N. Interaction between wheat germ RNA polymerase II and adenovirus 2 DNA. Evidence for two types of stable binary complexes. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3363–3371. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Ackerson J. W., Gralla J. D. Alterations in two conserved regions of promoter sequence lead to altered rates of polymerase binding and levels of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2709–2723. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Gralla J. D. Kinetic investigation of the mechanism of RNA polymerase binding to mutant lac promoters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10423–10430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Luse D. S., Segall J., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate initiation of transcription at the Ad2 major late promotor in a soluble system dependent on purified RNA polymerase II and DNA. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):469–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


