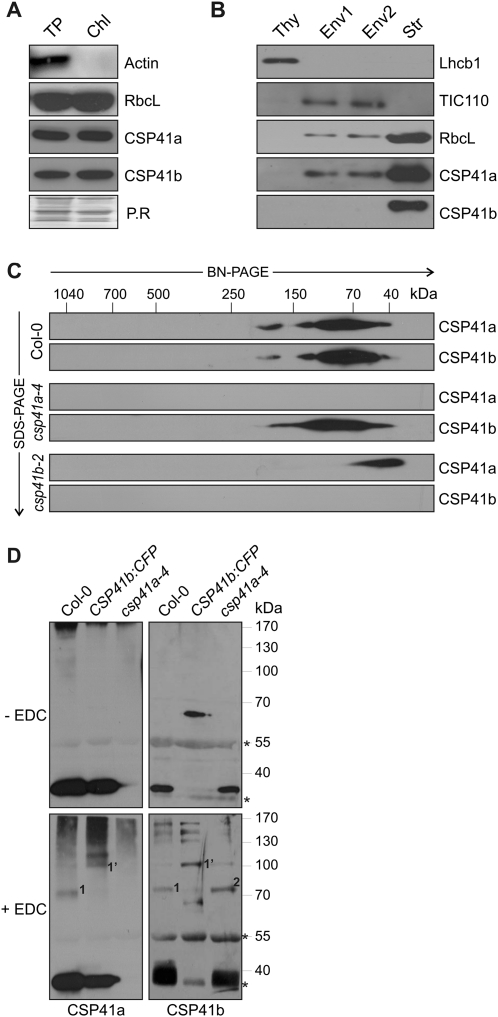
Fig. 3.
Characterization of complexes containing CSP41 proteins. (A) Total protein (TP) and chloroplast protein (Chl) extracts corresponding to 3 μg of Chl were subjected to SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies raised against CSP41 proteins. As controls, RbcL for chloroplast and actin for non-chloroplast proteins were used. As control, Ponceau Red stain (P.R.) of the membrane prior to antibody immunodecoration is shown. (B) Chloroplasts from WT plants were subfractionated into thylakoids (Thy), two envelope fractions (Env1 and Env2), and stroma (Str). Aliquots (40 μg) of proteins from each fraction were subjected to SDS–PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies raised against CSP41 proteins. As controls for the purity of the different fractions, antibodies recognizing Lhcb1, TIC110, and RbcL, which are located in thylakoids, envelope, and stroma, respectively, were used. (C) Stromal proteins from chloroplast samples corresponding to 30 μg of Chl were fractionated by BN-PAGE in the first dimension and by SDS–PAGE in the second. CSP41a and CSP41b were each detected using specific antibodies. The approximate molecular masses of the labelled protein complexes were estimated from the mobilities of other complexes with known molecular masses (Peltier et al., 2006). (D) Stromal proteins (70 μg) from WT (Col-0), csp41a-4 mutants, and a csp41b-2 line expressing CSP41b:CFP were cross-linked with EDC and fractionated by SDS–PAGE. Protein detection was carried out with specific antibodies as in A–C. Asterisks indicate unspecific bands detected by the CSP41b antibody.