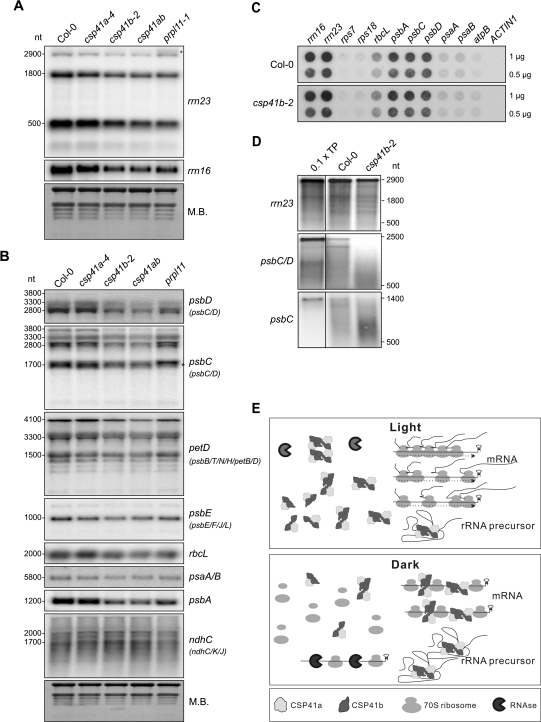
Fig. 7.
Lack of CSP41b affects the accumulation of chloroplast rRNAs and specific mRNAs. (A) Samples (20 μg) of total RNA from light-adapted WT (Col-0), csp41, and prpl11-1 mutant plants grown in the greenhouse (14 h/10 h light/dark regime at ∼180 μmol photons m−2 s−1) were size-fractionated by agarose gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose filters, and probed with cDNA fragments specific for the 5′ end of rrn23 and rrn16. Methylene blue (M.B.) staining of total leaf RNA served as loading control. The asterisk marks unprocessed rrn23. Quantification relative to WT can be found in Table 3. (B) Northern analyses of samples as in A with cDNA fragments specific for the coding regions of psbC, psbD, petD, psbE, rbcL, psaA/B, psbA, and ndhC. M.B. staining of total leaf RNA served as a loading control. (C) Run-on transcription in mature leaf chloroplasts isolated from WT and csp41b-2 plants. Duplicate nylon membranes were spotted with 1 μg or 0.5 μg of PCR products corresponding to the genes indicated at the top. Isolated chloroplasts were incubated in the presence of radiolabelled UTP. RNA from chloroplasts that had been pulse-labelled for 10 min was used to probe the membranes shown. The nuclear ACTIN1 gene was included as negative control. Quantification relative to rps18 can be found in Table 4. (D) Radiolabelled transcription products (TPs) from rrn23, psbC/D, and psbC were incubated with broken chloroplasts from WT and csp41b-2 mutants followed by re-isolation of RNA, separation on a denaturing 1.5% agarose gel, and transfer to nylon membranes. One representative of three independent experiments is shown. Note that in lane TP only one-tenth of the experimentally employed amount of transcription product was loaded. (A–D) Signals were analysed by autoradiography. (E) Working model for action of CSP41 protein complexes: in the light, newly synthesized rRNA precursors are rapidly incorporated into functional ribosomes, which in turn stabilize mRNAs during the translational process (arrows on ribosomes indicate translationally active ribosomes); CSP41 protein complexes do not bind to RNA. In the dark, CSP41 protein complexes associate with RNAs and protect them from nucleolytic cleavage. Untranslated RNA not stabilized by CSP41 protein complexes (i.e. in the csp41b and csp41ab double mutant) are degraded by RNases.