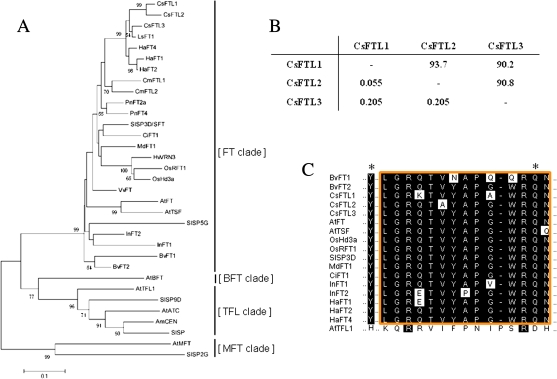
Fig. 1.
Cloning of FT-like genes from C. seticuspe. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on the deduced amino acid sequences of the PEBP gene family, including those of CsFTL1, CsFTL2, and CsFTL3, from several plant species. The tree was constructed by the Neighbor–Joining method. Bootstrap percentages >50% are shown along the branches. Species abbreviations: Antirrhinum majus, Am; Arabidopsis thaliana, At; Beta vulgaris, Bv; Citrus unshiu, Ci; Cucurbita maxima, Cm; Chrysanthemum seticuspe, Cs; Helianthus annuus, Ha; Hordeum vulgare, Hv; Ipomoea nil, In; Lactuca sativa, Ls; Malus×domestica, Md; Oryza sativa, Os; Populus nigra, Pn; Solanum lycopersicum, Sl; and Vitis vinifera, Vv. (B) Comparisons of CsFT paralogues. Ks and amino acid sequence identity (%) values for pairwise comparisons of CsFT paralogues are shown: Ks values are shown below the diagonal, while amino acid sequence identity (%) values are shown above the diagonal. (C) Partial amino acid sequence alignment of the PEBP family members. Asterisks indicate the residues Tyr85(Y)/Gln140(Q) and His88(H)/Asp144(D) contributing to FT and TFL1 functioning, respectively (Hanzawa et al., 2005; Ahn et al., 2006). The conserved segment region B in the fourth exon, corresponding to the external loop of the PEBP family proteins, is boxed. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)