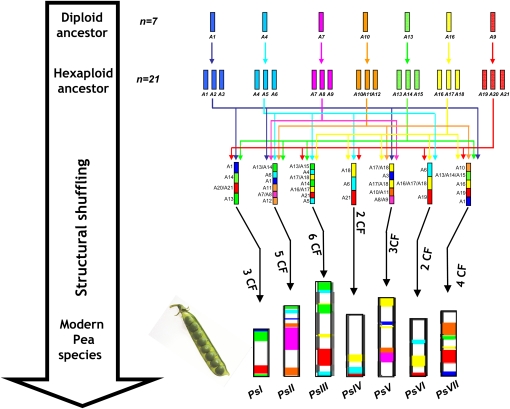
Figure 5 .
Pea genome paleo-history. The pea genome (bottom) is represented with a seven-color code to illuminate the evolution of segments from a common ancestor with seven chromosomes (A1–A7, top). Colored lines indicate the evolution of segments from a seven-chromosome common ancestor of the Eudicots to reach the modern pea genome structure. The 25 chromosomal fusions (CF) are highlighted with colored arrows. At the bottom of the figure is shown the actual pea genome structure. The ancestral shared duplications can be compared with the seven ancestral paleo-triplications reported in grape (Vitis vinifera, Abrouk et al. 2010): V. vinifera chromosomes are indicated by Vv, P. sativum linkage groups by Ps. 1Vv1-Vv14-Vv17/ PsIII-PsIV-PsV-PsVI-PsVII (yellow), Vv2-Vv12-Vv15-Vv16/PsI-PsII-PsV-PsVII (blue), Vv3-Vv4-Vv7-Vv18/PsI-PsII-PsIII-PsVII (green), Vv4-Vv9-Vv11/PsII-PsIII-PsIV-PsVI (light blue), Vv5-Vv7-Vv14/PsII-PsV (pink), Vv6-Vv8-Vv13/PsII-PsV-PsVII (brown), Vv10-Vv12-Vv19/PsI-PsIII-PsIV-PsVI-PsVII (red).