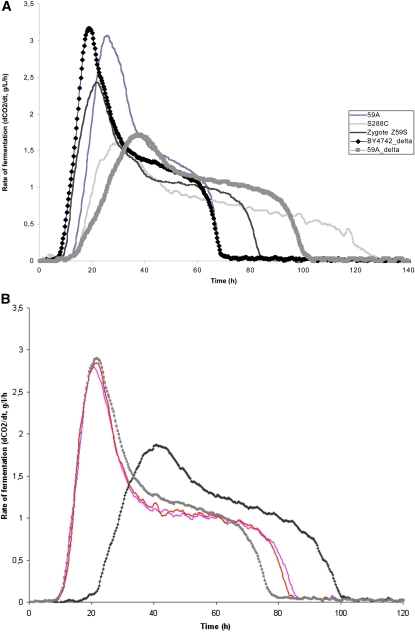
Figure 5 .
Reciprocal hemizygous analysis of ABZ1 and impact of p-aminobenzoate on the fermentation profiles. A) Fermentation rate profiles of the two reciprocal hemizygous strains carrying the ABZ1 allele from BY4742 or 59A. The hemizygous strains harbor either an active ABZ1 BY allele (strain BY4742/ABZ1-59A∆, thick gray line) or the 59A allele (strain 59A/ABZ1- BY4742∆, black line with diamonds). Profiles of the strains 59A (dark-blue line), the laboratory strain S288C (thin gray line), and the hybrid Z59S (black line) are shown. B) Impact of p-aminobenzoate on the fermentation profiles of hemizygous strains. Fermentation kinetics of two hemizygous strains in MS300 supplemented or not with 1 mg/l of p-aminobenzoic acid. Hemizygous strain carrying S288c ABZ1 allele in MS300 without (black line) or supplemented with p-aminobenzoic acid (gray kinetic line). Hemizygous strain carrying 59A ABZ1 allele in MS300, without (red kinetic line) or supplemented with p-aminobenzoic acid (pink kinetic line). The supplementation with p-aminobenzoic acid improves the fermentation capacity of the hemizygous strain carrying the S288c ABZ1 allele.