Figure 9 .
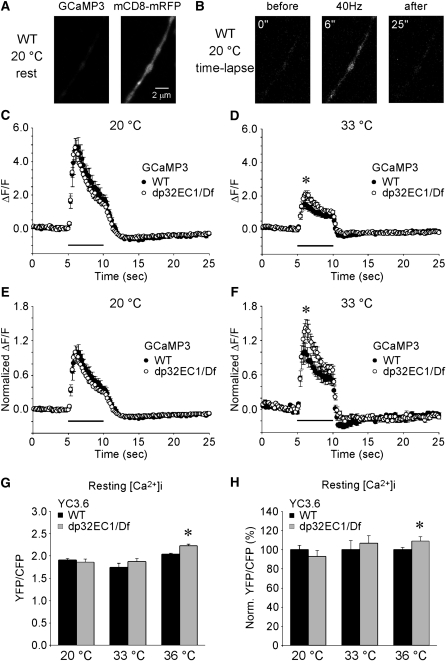
dp32EC1 exhibits conditional defects in presynaptic calcium signaling. (A–F) Imaging of cytosolic calcium transients within DLM neuromuscular presynaptic terminals expressing the calcium indicator GCaMP3. (A) A representative image of GCaMP3 at a resting WT synapse at 20°. Neuronal expression of the membrane-associated mCD8-mRFP protein provided a red fluorescent marker for nerve terminals. (B) Example images of GCaMP3 at WT synapses before, during, and after DLM motor axon stimulation (40 Hz for 5 sec) at 20°. Times indicated are relative to the start of the time-lapse imaging, and axon stimulation was initiated at 5 sec. (C–F) Fluorescence changes (ΔF/F) were examined at WT and dp32EC1 (dp32EC1/Df) synapses. (C) At 20°, DLM motor axon stimulation at 40 Hz for 5 s (bar above X axis) produced a similar increase in cytosolic calcium at WT (n = 11) and dp32EC1 (n = 17) synapses. In contrast, the same stimulation protocol at 33° (D) elicited a larger calcium transient in dp32EC1 (n = 13) than in WT (n = 14). The peak ΔF/F in dp32EC1 (3.09 ± 0.22) was significantly increased with respect to WT (2.48 ± 0.22). The data shown in C and D were normalized to the maximum ΔF/F in WT at each temperature and replotted in E and F, respectively. Asterisks in D and F indicate that the maximum ΔF/F in dp32EC1 is significantly greater than that in WT. (G, H) Imaging of relative resting presynaptic calcium concentrations within DLM neuromuscular presynaptic terminals expressing the ratiometric calcium indicator Cameleon YC3.6. The EYFP/ECFP emission ratio (YFP/CFP) was used to assess the relative resting presynaptic calcium concentrations at WT and dp32EC1 (dp32EC1/Df) synapses at 20°, 33°, and 36° (G). (H) The data shown in G were normalized to the mean YFP/CFP ratio in WT at each temperature. At restrictive temperatures, resting calcium was increased in dp32EC1 with respect to WT. As a percentage of WT, the resting calcium concentration at dp32EC1 synapses at 20° was 93 ± 4% (WT, n = 17; dp32EC1, n = 11). The corresponding values at 33° and 36° were 107 ± 4% (WT, n = 12; dp32EC1, n = 12) and 109 ± 2% (WT, n = 13; dp32EC1, n = 9), respectively.