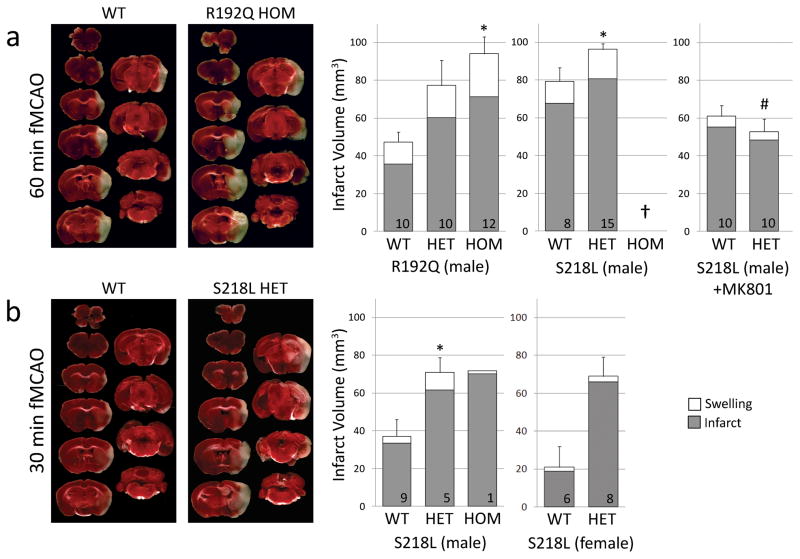
Figure 5.
FHM1 mutant mice develop larger infarcts after experimental stroke selectively attenuated by NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Left panel shows representative infarcts (unstained white tissue) 24 hours after fMCAO. Right panel shows infarct and ischemic swelling volumes (grey and white bars, respectively). a) After 60 minute fMCAO, infarcts were larger in both R192Q and S218L mutants compared to WT (p=0.007 and p=0.019, respectively). One of 9 WT, 8 of 23 S218L HET, and all 8 S218L HOM (†) mice died within 24 hours (Table 1), and were excluded from infarct volume analysis. Because genetic backgrounds and infarct volumes significantly differed between WT controls of the two mutant strains, we did not directly compare S218L and R192Q mutants in this study. MK-801 (1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally 15 minutes before fMCAO) significantly reduced infarct volume in S218L HET mutants (P<0.001 vs. untreated S218L HET shown in ‘a’) but not in the WT (P=0.061 vs. untreated WT shown in ‘a’). Therefore, MK-801 was more efficacious in FHM1 mutants (P=0.026 for infarct reduction by MK-801 between WT and FHM1 mutants). As a result, after MK-801, infarct and swelling volumes were comparable between WT and S218L HET mice (P=0.367), as were neurological outcomes (Table 1). b) Thirty minute fMCAO also resulted in larger infarcts in male and female S218L mutants compared to WT (p=0.028). Despite shorter ischemia, 3 of 4 S218L HOM mutants died within 24 hours and were again excluded from infarct volume analysis; the data from the only surviving HOM mutant are shown. There was no mortality in WT and HET groups after 30 min fMCAO. Numbers of mice are shown on each bar. Standard error bars and p values refer to total volume (i.e., infarct plus swelling). *p<0.05 vs. WT, #p<0.05 vs. untreated S218L HET after 60 min fMCAO.