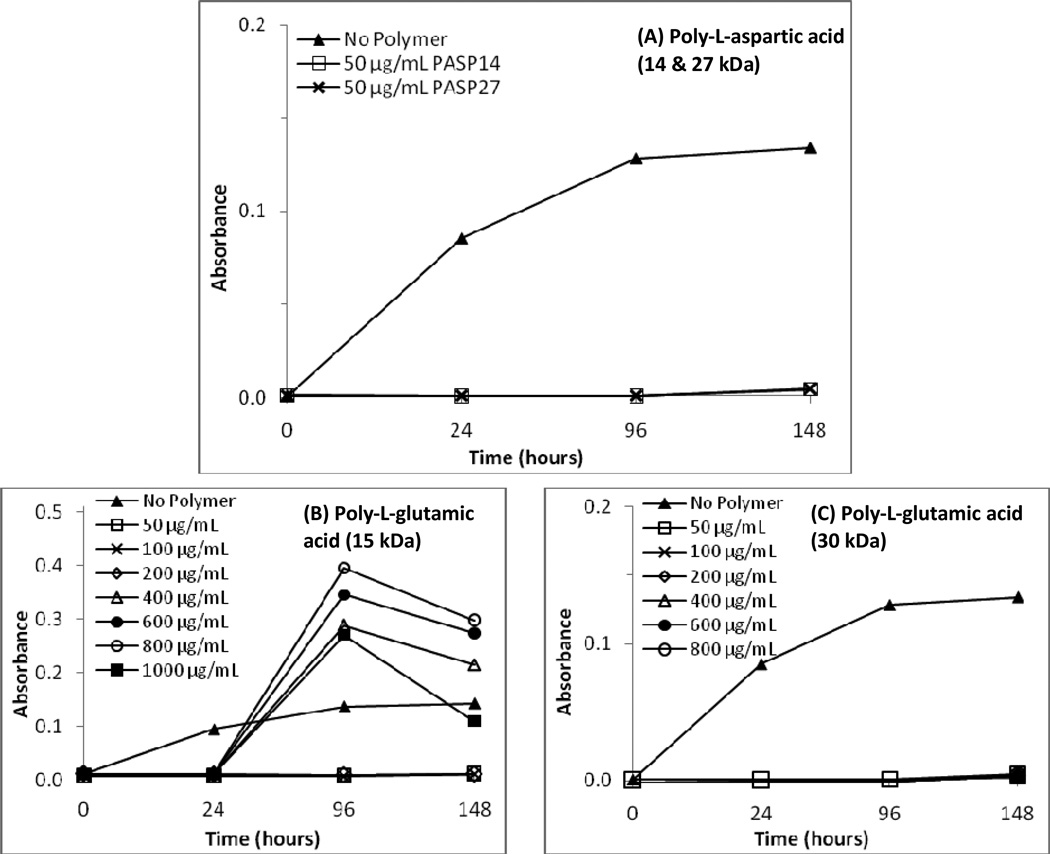
Figure 1.
Effects of polyaspartic and polyglutamic acid concentrations in a supersaturated calcium-phosphate (CaP) solution. (A) Optical density profiles of the CaP solutions containing 50 µg/mL of 14 kDa or 27 kDa poly-L-aspartic acid (PASP14 or PASP27, respectively). (B) Optical density profiles of the CaP solutions containing 0–1,000 µg/mL 15 kDa poly-L-glutamic acid (PGLU15). The lines for concentrations 50–200 µg/mL are overlapping near the zero value. (C) Optical density profiles of the CaP solutions containing 0–800 µg/mL 30 kDa poly-L-glutamic acid (PGLU30). The lines for all concentrations are overlapping near zero.