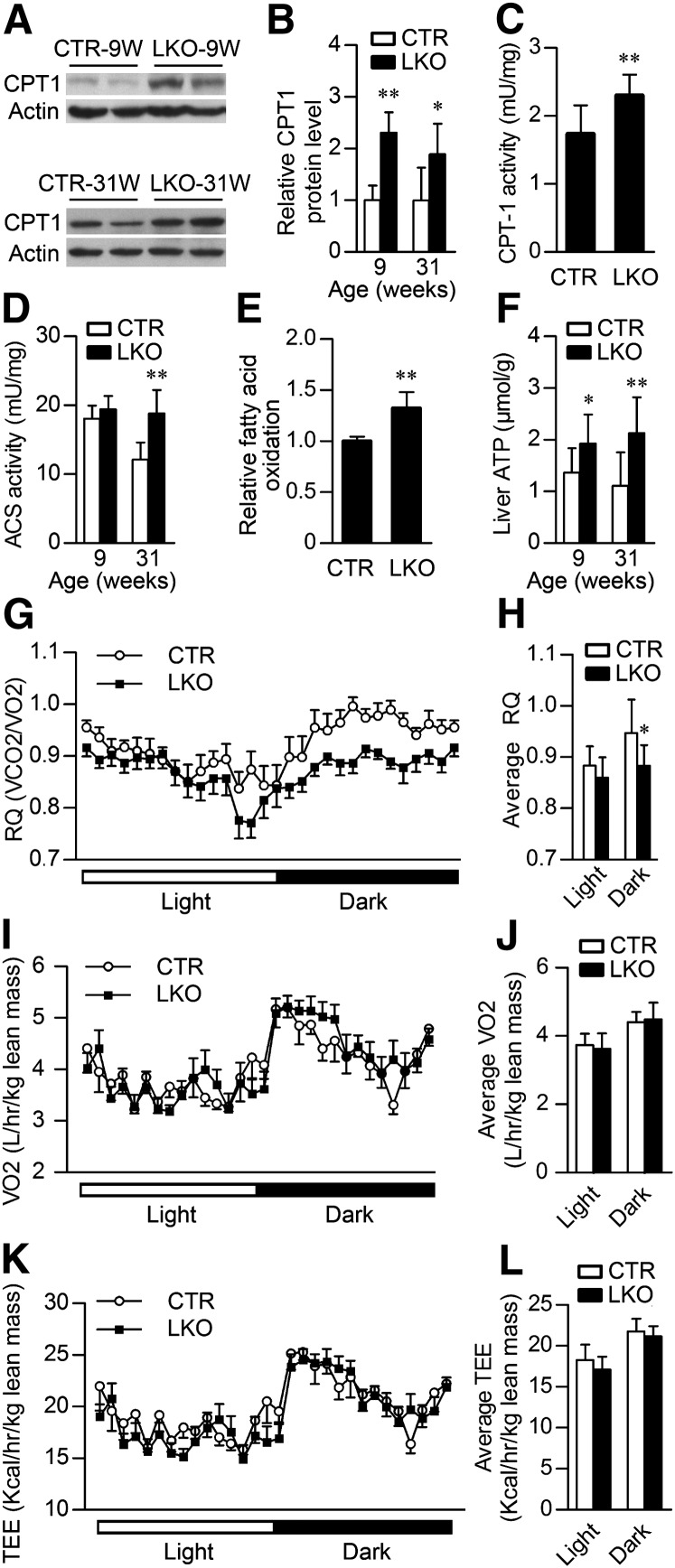
Fig. 6.
Hepatic Patt1 deficiency increases fatty acid oxidation in liver. (A) The protein level of CPT-1, the rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid oxidation, was upregulated in the liver of 9- and 31-week-old male Patt1 LKO mice as measured by immunoblot. (B) Quantification of CPT-1 protein levels in (A). n = 4–6/group. (C) CPT-1 activity in the liver of male Patt1 LKO mice was upregulated. n = 8. Liver mitochondria were extracted from 10-week-old male Patt1 LKO mice and littermate controls to measure CPT-1 activity. (D) The enzyme activity of ACS, a crucial enzyme catalyzing the prestep reaction for β-oxidation of fatty acids, was upregulated in the liver of 31-week-old Patt1 LKO mice compared with littermate controls. n = 8/group. (E) Fatty acid oxidation in hepatocytes of Patt1 LKO mice was increased as determined by the liberation of 3H2O from 3H-palmitic acid oxidation. Mouse primary hepatocytes were prepared from mice at ages 10–15 weeks. (F) At 9 and 31 weeks of age, male Patt1 LKO mice exhibited elevated hepatic ATP levels after 6 h fasting. n = 8–12/group. (G–L) At 22 weeks of age, male Patt1 LKO mice showed decreased respiratory quotient (RQ), similar oxygen consumption (VO2), and total energy expenditure (TEE) at night when measured by a comprehensive laboratory animal monitoring system. n = 10/group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.