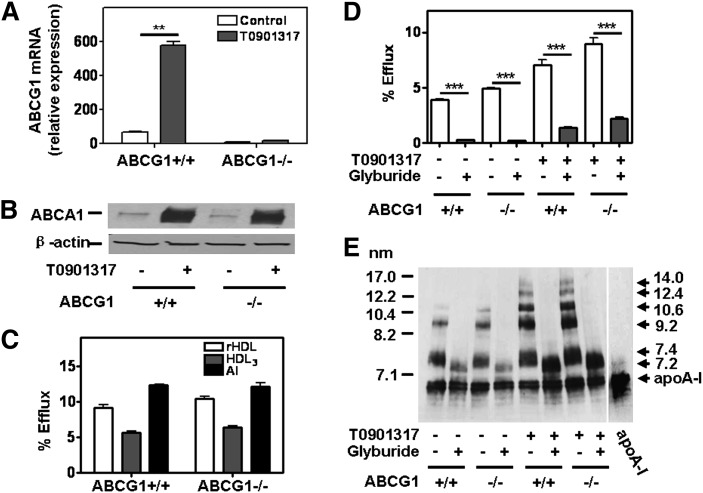
Fig. 4.
Role of ABCG1 in nascent HDL particle formation and cholesterol efflux in primary hepatocytes. Primary hepatocytes from ABCG1+/+ and ABCG1−/− mice were treated with and without LXR agonist T0901317 (5 µM) for 16 h, and then with or without glyburide (500 µM) for 1 h as described in Fig. 2. Cells were then incubated in the presence or absence of glyburide with 20 µg/ml human apoA-I for 16 h. A: ABCG1 mRNA expression was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. The ct values for ABCG1 expression under basal and activated conditions were 26.64 ± 0.23 and 23.08 ± 0.09, respectively, and (B) ABCA1 expression was determined by Western blot analysis. C: Hepatocytes were labeled with 0.2 µCi/ml [3H] cholesterol for 48 h. Cells were treated with T0901317 for 16 h. Following incubation with 20 µg/ml rHDL, human HDL3, and human apoA-I for 16 h, radioactivity in the medium and cells was determined. Cholesterol efflux was calculated as the percentage of counts in the medium relative to the total counts in the medium and cells together. Values shown were the mean ± SEM of triplicate determinations. D: Hepatocytes were labeled with 0.2 µCi/ml [3H] cholesterol for 48 h. Cells were treated with T0901317 and glyburide as indicated. Following incubation with 20 µg/ml human apoA-I for 16 h, radioactivity in the medium and cells was determined. Cholesterol efflux was calculated as the percentage of counts in the medium relative to the total counts in the medium and cells together. Values shown were the mean ± SEM of triplicate determinations. E: ApoA-I lipidation was assessed by separating cell culture medium (5 µl) by nondenaturing GGE and immunoblotting with anti-human apoA-I. Results are representative of three experiments. Significance at **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001.