Figure 1.
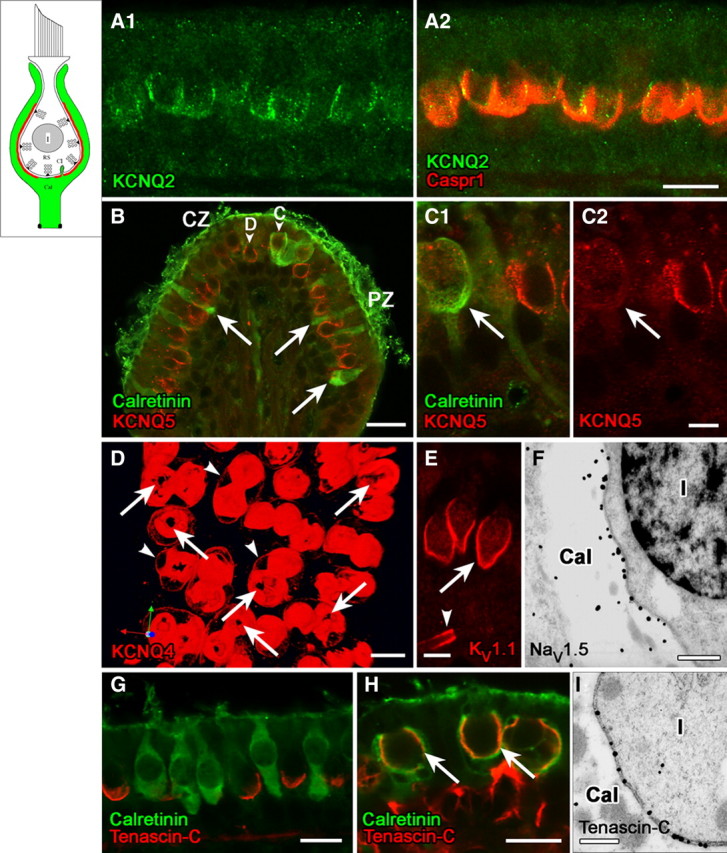
Domain 1 of the calyx ending, facing the zone of presynaptic ribbons (RS) in the type I hair cell, is strongly immunoreactive for voltage-gated K and Na channels and associated proteins. Schematics in the upper left corner of Figures 1–4 delineate the successive domains in red. A, KCNQ2 immunostaining (A1, green) on the inner surface of the calyx ending, where it colocalized with Caspr1 (A2, red). B, C, KCNQ5 antibody (red) labeled the inner surface of calyces of both central-zone (CZ) and peripheral-zone (PZ) dimorphic (D) afferents (B, C1, C2, calretinin-negative), but not calyx-only (C) afferents (B, C1). Calretinin antibody (B, C1, green) selectively labels type II hair cells (arrows) and calyx-only (C) afferents, not dimorphic (D) afferents. Localization of the KCNQ5 label to the calyx membrane (rather than, e.g., the hair-cell membrane) was determined by immunogold EM (data not shown). D, Top view of a whole-mount utricular macula, stained with KCNQ4 antibody (red). The antibody stained the calyx membrane intensely on its inner face (domain 1) and lightly on its outer face (arrowheads, domain 3, see below). Interruptions in the KCNQ4 immunostaining at the bottom of each calyx appear as black holes (arrows). E, Antibodies to KV1.1 (red) and KV1.2 (similar pattern but not shown) also label domain 1 (arrow) in all calyces, in addition to labeling membrane of the nerve fiber near the first internode (the juxtaparaheminodal membrane, arrowhead). F, Immunoreactivity for NaV1.5 subunit was restricted to the calyx inner membrane, as shown here for a calyx (Cal) surrounding a type I hair cell (I); the calyx belonged to a dimorphic afferent in the peripheral zone of a crista. G, Antibody to tenascin-C (red) formed cup-like labeling at the base of type I hair cells, but not calretinin-positive type II hair cells (green) in the extrastriolar (peripheral) zone of the utricular macula. H, Tenascin-C forms much larger cups on these striolar calyces than on the extrastriolar calyces of G. Staining for tenascin-C (red) and calretinin (green) overlaps in confocal images, producing a yellow color in domain 1 (arrows) of calyx-only afferents in the striolar (central) zone. Tenascin-C antibody also labeled extracellular matrix in the tissue stroma below the sensory epithelium (see red stain below right-hand calyces). I, The higher resolution of immunogold EM revealed that tenascin-C is neither in the hair cell nor in the calyx, but rather in the synaptic cleft between the two (thus, the overlap in tenascin-C and calretinin in H reflects proximity of the antigens rather than colocalization, an underappreciated likelihood in most confocal studies). Shown are tenascin-C-immunolabeled gold particles in the synaptic cleft of a calyx in a crista peripheral zone. Such particles were not seen in the synaptic clefts of bouton synapses on type II hair cells (not shown). Scale bars: A, D, G, H, 10 μm; B, 20 μm; C, E, 5 μm; F, I, 500 nm.
