Figure 5.
GPR179 Mutations Are Present in Two Probands with Autosomal-Recessive cCSNB
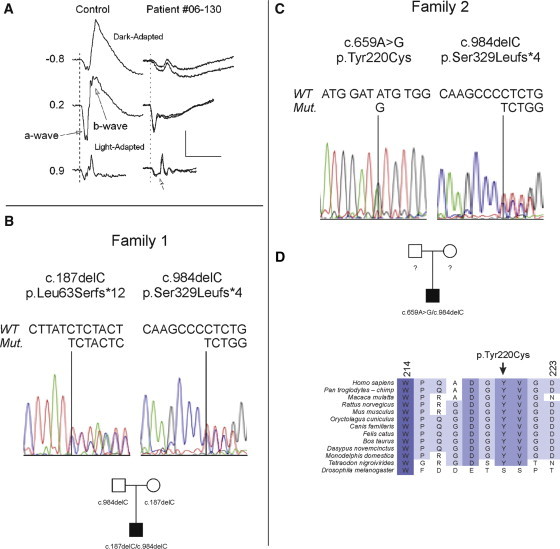
(A) ERGs obtained from a control subject and proband 1 for a standard series of stimulus conditions that allow rod- and cone-mediated responses to be evaluated. For proband 1 (patient 06-130), the two records indicate ERGs obtained from the two eyes. Under dark-adapted conditions, ERGs obtained from the proband had markedly reduced b-waves. Under light-adapted conditions (30 cd/m2), the cone ERG had a squared a-wave (arrow). Values indicate flash luminance in log cd s/m2.
(B and C) GPR179 (accession number NM_001004334.2) exons were sequenced from DNA samples isolated from 44 patients with cCSNB. Chromatograms containing the mutant sequences found in probands 1 (B) and 2 (C). In addition to the chromatogram, each subsection shows the mutation, the predicted impact on the amino acid sequence, and the segregation pattern. The pedigree for proband 1 shows that he inherited one mutant GPR179 allele from each parent (c.187delC and c.984delC), who had normal vision (data not shown). The parents of proband 2 were not available for analyses.
(D) Comparison of the region of GPR179 containing the amino acid substitution (p.Tyr220Cys) identified in proband 2 across phyla. With the exception of Drosophila melanogaster, Tyr220 is conserved for every species for which data were available. In general, this region of the protein is highly conserved (the shade of blue indicates the amount of conservation; dark blue indicates the most conserved). The study followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committee of the Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam. All participants provided signed informed consent for participation in the study.
