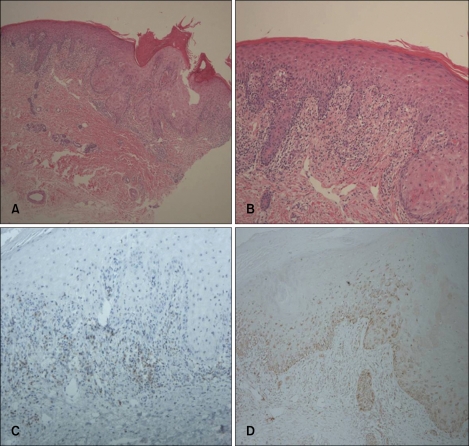
Fig. 2.
(A, B) Acanthosis, parakeratosis, spongiosis, lymphocyte exocytosis, and the presence of necrotic keratinocytes in the epidermis. Vacuolar alterations at the dermo-epidermal junction are evident. Infiltration by lymphocytes and a smaller number of eosinophils, and extravasation of red blood cells are observed in the superficial dermis (H&E; ×40, ×100). (C, D) The intraepidermal lymphocytes are primarily CD8+ T cells; and the dermal perivascular and interstitial lymphocytes, primarily CD4+ T cells (C: CD4, D: CD8, ×100).