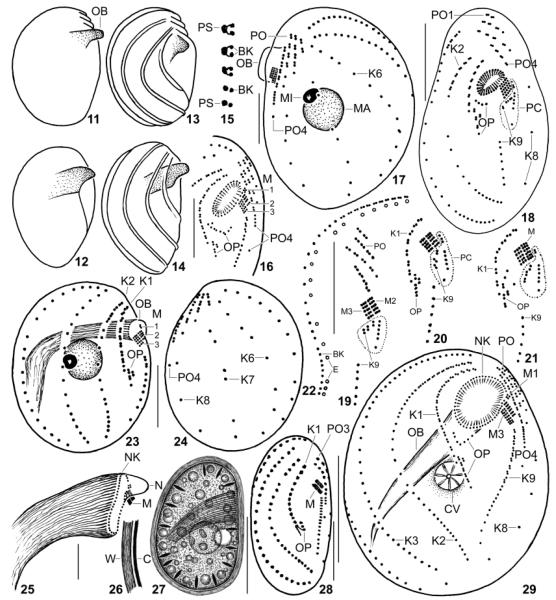
Fig. 11–29.
Leptopharynx bromelicola n.sp. (11–17, 22–29) and Leptopharynx costatus (18–21) from life (11, 12, 26, 27), redrawn from scanning electron microscopy micrographs (13, 14), after silver nitrate impregnation (15), and after protargol impregnation (16–25, 28, 29). 11–14. Variability of macrostome body shape; cortical ridges not shown in Fig. 11, 12. 15. Structure of kinety 2. 16, 29. Ventral views of a microstome (16) and of a transition stage (29) to a macrostome, where the oral basket opening is broadly elliptical due to insufficient fixation. 17. Left side view of a transition stage showing the preoral kineties on the left side. 18–21. L. costatus, ventral overview (18, from Foissner 1989) and details (19–21, originals from same population), showing the location and variability of the postoral complex (PC, encircled by dotted line), which is absent from L. bromelicola. 22. Arrangement of basal bodies and extrusomes in kinety 2. 23, 24. Right and left side view of microstome hapantotype, length 28 μm; drawn to scale relative to the macrostome shown in Fig. 8, 9. 25. Oral basket of a macrostome. 26, 27. Right side view of a macrostome resting cyst. 28. Ventral view of a microstome resting cyst. BK, basal body; C, cortex; CV, contractile vacuole; E, extrusomes; K1–9, somatic kineties; M(1–3), adoral membranelles; MA, macrostome; MI, microstome; N, nose; NK, nasse kinetosomes; OB, oral basket; OP, oral primordium; PC, postoral complex; PO(1–4), preoral kineties; PS, parasomal sac; W, cyst wall. Scale bars = 10 μm (Fig. 16–18, 23–25, 28) and 20 μm (Fig. 22, 27, 29).