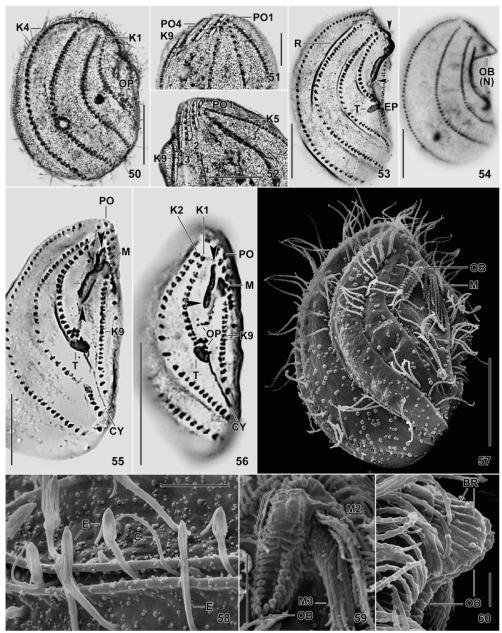
Fig. 50–60.
Leptopharynx bromelicola n. sp., macrostome (50–55, 58–60) and microstome (56, 57) specimens after Klein–Foissner (50–52) and Chatton–Lwoff (53–56) silver nitrate impregnation, and in the scanning electron microscopy (57–60). 50, 53, 54. Right side views, showing the dense ciliation of kineties 1–4, the dense cortical granulation (50), and the large oral basket (53, ends marked by arrowheads) with a distinct nose (54). The asterisk marks kineties 1 and 2 greatly widening posteriorly. 51, 52. Ventrolateral view showing a narrowly meshed silverline pattern associated with the preoral kineties and the anterior portion of kinety 9. 55, 56. Ventral view showing macrostomes and microstomes differing mainly in the length of the oral basket opening (arrowheads) and the number of basal bodies. The lines (55) indicate the width of the basket opening, while the asterisk denotes the transition site of long and short basket rods. 57. Ventrolateral view of a microstome postdivider with oral basket marked by arrowhead. 58. Part of left side, showing exploding extrusomes within and between the cortical furrows. 59, 60. Frontal and lateral view of oral basket, which is covered by a membranous structure in the upper, nose-forming half (bracket). Scale bars = 2 μm (Fig. 60), 5 μm (Fig. 58, 59), 10 μm (Fig. 51, 52), 15 μm (Fig. 57), and 20 μm (Fig. 50, 53–56). Explanation of abbreviations for Fig. 43–60: BR, basket rods; C, cilium; CY, cytopyge; E, extrusomes; EP, excretory pore; K1–9, somatic kineties; MA, macrostome; MI, microstome; M(1–3), adoral membranelles; NK, nasse kinetosomes; OB, oral basket; OP, oral primordium; PO(1–4), preoral kineties; R, cortical ridge; T, excretory tube.