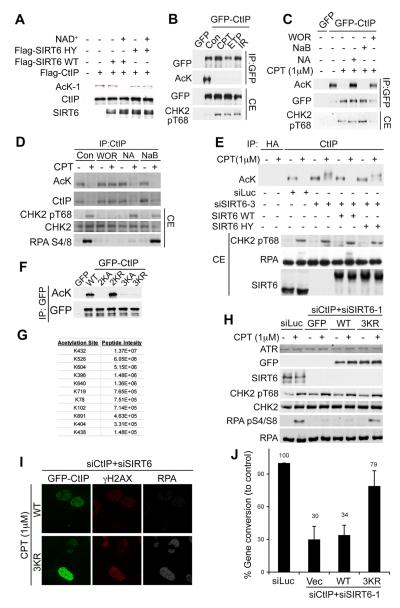
Fig. 4.
SIRT6 deacetylates CtIP to promote resection and HR. (A) Constitutive CtIP acetylation is removed by SIRT6 in vitro. (B) GFP-CtIP is acetylated in HEK293 cells and deacetylated upon treatment with CPT (1μM), etoposide (1μM) or IR (10Gy). Immunoprecipitated material and cell extract (CE) were analysed. (C) NA or WOR block GFP-CtIP de-acetylation in HEK293 cells after DNA damage. (D) Endogenous CtIP is acetylated in U2OS cells. A negative-control IP is shown in fig. S12D. (E) SIRT6 mediates CtIP deacetylation upon DNA damage. CtIP acetylation status in U2OS cells stably expressing siRNA-resistant GFP-SIRT6. (F) Identification of CtIP acetylation sites; mutations were introduced into GFP-CtIP and analysed by IP-WB. Mutants: 2KA (K513A+K515A), 2KR (K513R+K515R), 3KR (K432A+K526A+K604A) and 3KR (K432R+K526R+K604R). (G) Mass-spectrometry data for intensity of acetylated CtIP peptides. (H) Non-acetylatable CtIP (3KR) alleviates resection defects caused by SIRT6 depletion. U2OS cells expressing siRNA-resistant GFP-CtIP (WT/3KR), where SIRT6 and CtIP were depleted, were treated with CPT and analysed. (I) U2OS cells treated as in (H) were analysed by IF. (J) CtIP-3KR mutant partially rescues HR defect of SIRT6 depleted cells. Cells contain with vector (Vec), Flag-CtIP-WT or 3KR. Data are from two experiments.