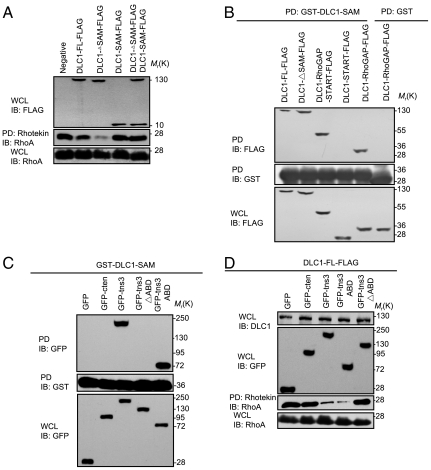
Fig. 3.
The tensin3 ABD binds to the SAM domain of DLC1 to activate its Rho-GAP function. (A) Effects of the FL and different segments of DLC1 on RhoA activation, respectively. HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated constructs and the corresponding whole cell lysates (WCL) were analyzed for RhoA activation. An aliquot of the WCL was subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis with anti-FLAG and anti-RhoA to show the levels of the FLAG-tagged proteins and the total RhoA. (B) The SAM domain binds to the Rho-GAP domain in DLC1. HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated constructs were subjected to pull-down with glutathione beads coupled to GST-DLC1-SAM or GST alone, and the bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by IB with anti-FLAG (Top). The GST proteins were verified by probing the membrane with anti-GST antibody (Middle). The expression levels of the different constructs were assayed by an anti-FLAG blot (Bottom). (C) The DLC1 SAM domain binds to the tensin3 ABD domain. HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated constructs were subjected to pull-down with GST-DLC1-SAM. The bound proteins were detected in an anti-GFP blot. (D) The ABD domain of tensin3 is sufficient for activating DLC1. The FL or a truncated version of tensin3 (as GFP fusion) was coexpressed with DLC1-FLAG in HEK293 cells and the effect on RhoA activity was subsequently assessed. Similar levels of GFP proteins and total RhoA were confirmed by the corresponding immunoblots. All scanned films are representative of three independent experiments.