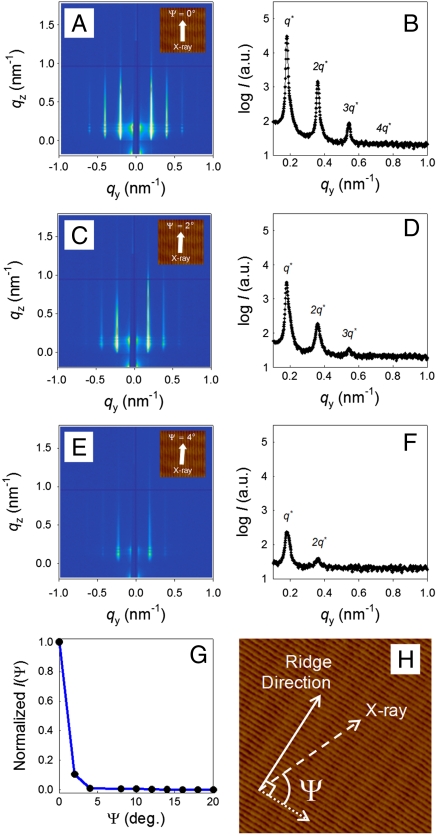
Fig. 4.
GI-SAXS patterns of PS-b-PEO thin films on the faceted sapphire substrate. (A) The X-ray beam follows the (1 0) lattice line. From this point, the sample stage is rotated to 2° (C) and 4° (E). The line profiles of scattering as a function of the scattering vector in (B), (D), and (F) are corresponding to (A), (C), and (E), respectively. qy is the in-plane scattering vector. (G) Plot of the integrated intensities of the first-order reflection as a function of rotation angle. These data were used to calculate the orientation parameter with respect to the normal of the ridge direction. (H) Schematic representation for defining rotation angle, Ψ.Ψ is defined as the angle between the direction of the X-ray beam and the direction of cylindrical BCP microdomains.