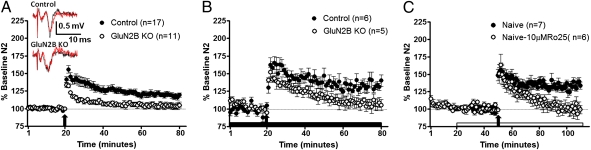
Fig. 3.
GluN2B is necessary for LTP in dlBNST. (A) Averaged time course of synaptic field potentials after high-frequency stimulation (at arrow; two 1-s trains at 100 Hz) in dlBNST from GluN2B KO and control (single-transgene and WT littermates) mice. (Inset) Representative traces of control and GluN2B KO mice before tetanus (red) and 60 min after tetanus (black). (B) Averaged time course of synaptic field potentials after high-frequency stimulation (at arrow; two 1-s trains at 100 Hz) in dlBNST from GluN2B KO and control (single-transgene and WT littermates) mice in the presence of picrotoxin (25 μM). (C) Averaged time course of synaptic field potentials after high-frequency stimulation (at arrow; two 1-s trains at 100 Hz) in dlBNST from naive adult male C57BL/6J mice. RO25-6981 (10 μM, a GluN2B-selective antagonist) was applied 30 min before tetanus and throughout the remainder of the experiment.