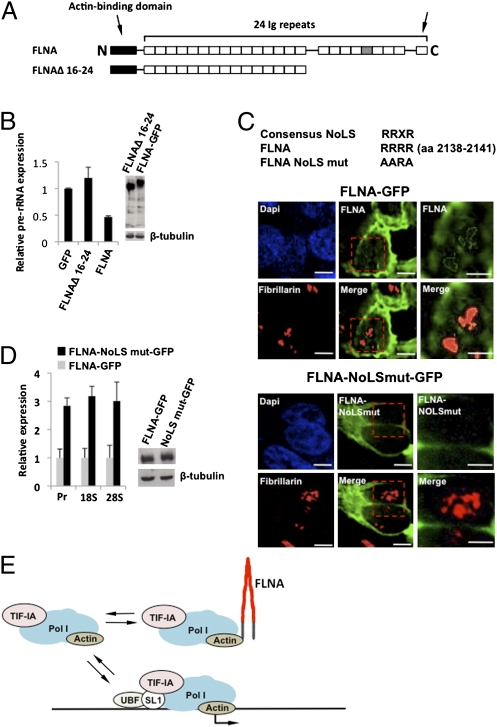
Fig. 5.
FLNA contains a nucleolar localization sequence in the C-terminal region. (A) Domain structure of FLNA depicting the C-terminal deletion (FLNAΔ 16–24). Ig repeat 20, containing the NoLS, is colored gray, the arrow on the right indicates the dimerization domain. (B) qRT-PCR demonstrating that the FLNA C-terminal region is required for suppression of rRNA expression. 293T cells stably transduced with FLNA siRNA (Fig. S2D) were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated proteins and isolated by flow cytometry before qRT-PCR analysis. (C) Microscopic analysis demonstrating the loss of nucleolar retention after mutation of the NoLS in FLNA. The NoLS motif in Ig repeat 20 of the human FLNA (RRRR) was mutated (AARA) in the full-length FLNA fused to GFP as depicted. 293T cells stably transduced with FLNA siRNA were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated proteins and isolated by flow cytometry before qRT-PCR analysis. For microscopic analysis, GFP and fibrillarin expression were detected at 24 h posttransfection. Images were obtained using a Delta Vision (Applied Precision) microscope. Higher magnifications of the red outlined boxes in Center are shown in Right. (Bars: 10 μm, Left and Center; 5 μm, Right.) (D) qRT-PCR demonstrating that mutation of the NoLS relieves the suppressive effect of FLNA on rRNA expression. 293T cells stably transduced with FLNA siRNA were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated proteins and isolated by flow cytometry before qRT-PCR analysis. (E) Model depicting the proposed mechanism by which FLNA suppresses rRNA transcription.