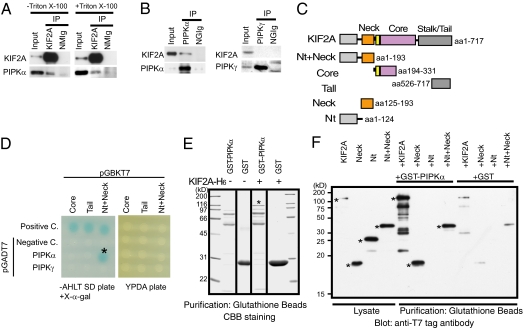
Fig. 1.
Identification of a direct interaction between KIF2A and PIPKα. (A and B) Western blot analysis of fractions immunoprecipitated by anti-KIF2A (A) and anti-PIPKα or anti-PIPKγ (B) antibodies. Immunoprecipitation (IP) by the anti-KIF2A antibody was performed with (+) or without (–) 1% Triton X-100. The S2 fraction including 30 μg of protein (Input), or the eluted fraction corresponding to 0.5 μg of anti-KIF2A antibody (KIF2A), anti-PIPKα antibody (PIPKα), anti-PIPKγ antibody (PIPKγ), normal mouse IgG (NMIg), or normal goat IgG (NGIg), was loaded in each lane. (C) Constructs of KIF2A used for the assays. (D) Yeast two-hybrid analyses of the direct interactions between baits and preys. pCL1, an expression vector for full-length GAL4, and pGADT7 vectors were used for the positive and negative control (Positive C. and Negative C.), respectively. Transformants were plated on SD agar plates without adenine, histidine, leucine, and tryptophan (−AHLT) supplemented with X-α-gal (Left) and YPDA agar plate (Right). (E) In vitro binding assays. KIF2A-(His)6 (asterisk) bound specifically to GST-PIPKα–conjugated beads but not to GST-conjugated beads. (F) Western blot analysis with anti-T7 tag antibody of binding assay reactions using deletion constructs of KIF2A. Each fragment is indicated in C. KIF2A proteins are indicated by asterisks.