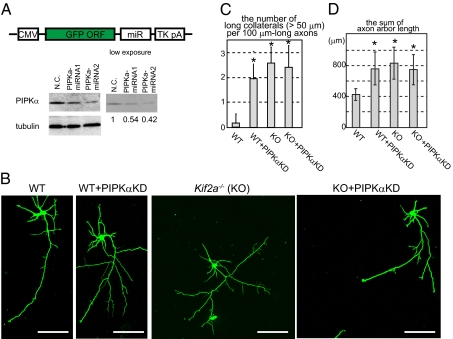
Fig. 4.
Morphological phenotypes in PIPKα-knockdown and/or KIF2A-knockout hippocampal neurons. (A) Schematic of the knockdown vector design (Upper) and its effects (Lower). GFP and microRNA (miR) cassete were expressed by the CMV promotor and polyA signal from Thymidine kinase (TK pA). Negative control (N.C.) and miRNA vectors were transfected, incubated for 3 d and analayzed by Western blot. Numbers under the Western blot data indicate the relative intensities of the Western blot experiment. (B–D) Inhibition of PIPKα or KIF2A resulted in elongated collateral branches in hippocampal neurons. Cells were transfected by the negative control vector or the miRNA vector (PIPKαKD) using electroporation when they were plated, cultured for 3 d, fixed, and observed by GFP signals. (B) Representative images of hippocampal neurons. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (C) The number of collaterals longer than 50 μm was counted per 100 μm-long axons. Data are shown as mean ± SD; *P < 0.01, Student's t test; 30 neurons from three independent mice. (D) The total lengths of axons were calculated. Data are shown as mean ± SD; *P < 0.01, Student's t test; 30 neurons from three independent mice.