Figure 1.
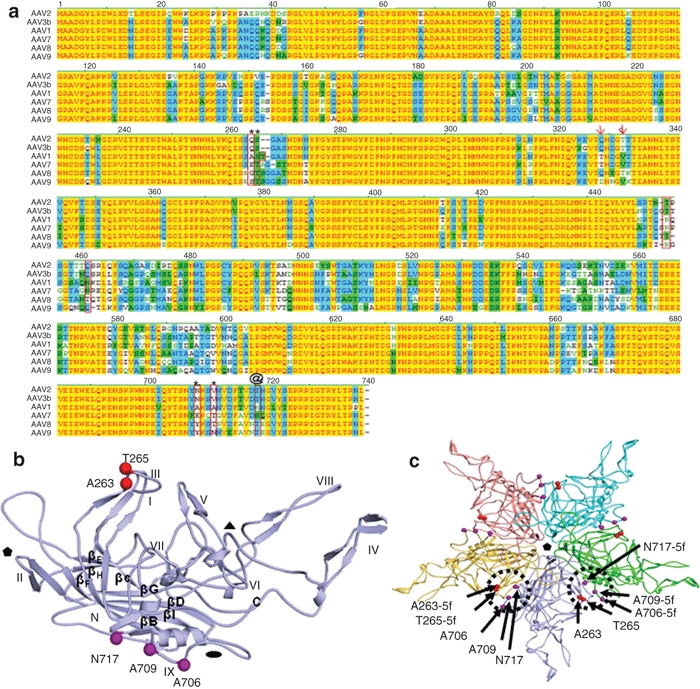
Amino acid candidates responsible for efficient skeletal muscle transduction. (a) Capsid amino acids of low skeletal muscle transducing serotypes (AAV2, AAV3) versus high skeletal muscle transducers (AAV1, AAV6, AAV7, AAV8, AAV9) were aligned using the Vector NTI program (Invitrogen). Alignments were examined for distinct amino acids of AAV2 from the others. See text for additional modeling criteria. Amino acids boxed or marked with arrows were deemed to be of interest. AAV2.5 is composed of the five amino acids indicated by * and @. (b) Location of the five amino acids on a single VP subunit which were modified in the AAV2.5 variant. Notice that the five amino acids are located on opposite positions of one subunit. (c) Location of the same five amino acids (circles and arrows) in the context of an assembled AAV capsid pentamer. Notice that the five amino acids are now in close proximity when two subunits are assembled. The five amino acid changes are located near the twofold axis of symmetry. AAV, adeno-associated virus.
