Figure 4.
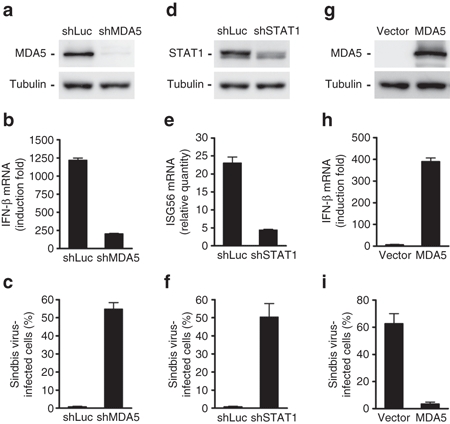
Modulation of the IFN response can change cellular susceptibility to SBV infection. Hep3B cells, which are not susceptible to SBV infection, were converted to be susceptible by knocking down the expression of MDA5 or STAT1. Conversely, 293T cells, which are susceptible to SBV infection, were converted to be more resistant to SBV infection by overexpressing MDA5. (a,d) The protein levels of MDA5 or STAT1, respectively, in Hep3B cells knocked down by shRNA. (b) Reduced IFN-β mRNA expression in response to poly(I:C) stimulation in the Hep3B cells with MDA5 knockdown. (e) Reduced ISG56 mRNA expression in response to IFN-α stimulation in Hep3B cells under STAT1 knockdown. (c,f) Increased susceptibility to SBV infection in Hep3B cells under MDA5 or STAT1 knockdown, respectively. (g) Protein levels of ectopic MDA5 expression in 293T cells. (h) Increased IFN-β mRNA synthesis in response to poly(I:C) stimulation in 293T cells overexpressing MDA5. (i) Reduced susceptibility to SBV infection in 293T cells overexpressing MDA5. IFN, interferon; SBV, Sindbis virus.
