Figure 1.
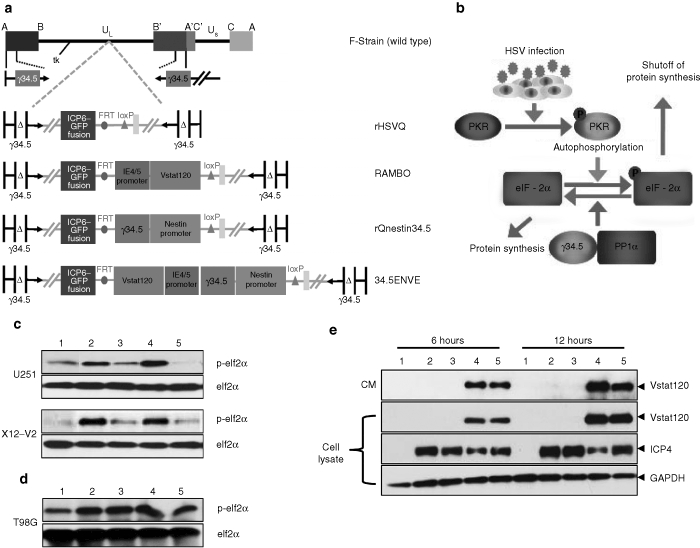
Structure and characterization of 34.5ENVE. (a) Genetic map of wild-type herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), and the various oncolytic viruses (OVs) used in this study. (b) Activation of PKR upon OV infection causes phosphorylation of eIF2α, and subsequent shutoff of protein synthesis. Viral ICP34.5 activates protein phosphatase 1α, to reverse phosphorylation of eIF2α and the subsequent protein translation. (c) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated and total eIF2α in high nestin-expressing U251 and X12-V2 glioma cells treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (lane 1) or infected with rHSVQ1 (lane 2), rQnestin34.5 (lane 3), RAMBO (lane 4), or 34.5ENVE (lane 5) [multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 0.1], 24 hours postinfection. (d) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated and total eIF2α in low nestin-expressing T98G glioma cells treated similarly (MOI = 0.1), 24 hours postinfection. (e) Western blot analysis of U251 glioma cells treated with PBS (lane 1), rHSVQ1 (lane 2), rQnestin34.5 (lane 3), RAMBO (lane 4), or 34.5ENVE (lane 5) at an MOI = 0.1. The cells were harvested at 6 and 12 hours postinfection and analyzed for expression of secreted and cellular Vstat120 and ICP4. Note the presence of Vstat120 in cells infected with RAMBO and 34.5ENVE.
