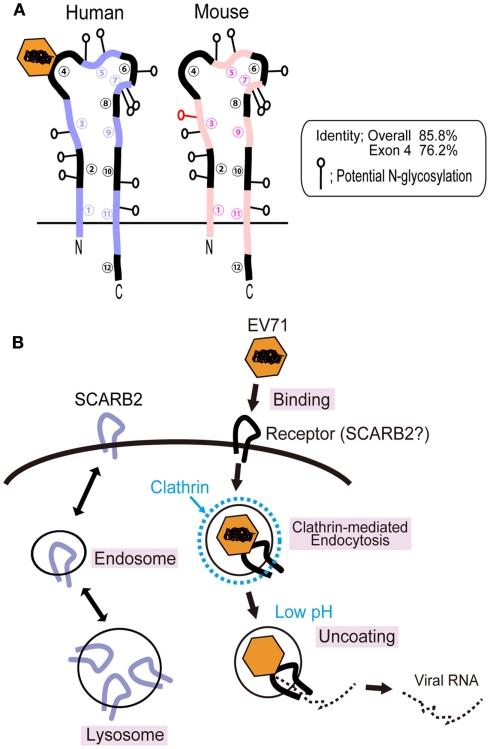
Figure 2.
Scavenger receptor class B, member 2 and EV71 infection in RD cells. (A) Comparison of the structures of human and mouse SCARB2. The human and mouse SCARB2 proteins are type III transmembrane proteins consisting of 478 amino acids. The amino acid identity of human SCARB2 to mouse SCARB2 is 85.8%. Because mouse SCARB2 does not serve an efficient receptor, it is possible to identify the virus binding site using chimeric receptors including mouse and human sequences. The 63-amino-acid region that is encoded in exon 4 of the human SCARB2 gene plays an essential role in EV71 binding and infection. (B) Mechanism of EV71 infection in RD cells. The SCARB2 protein is located in the lysosomal and endosomal compartments and shuttles to the plasma membrane. This protein is able to bind EV71 when present at the cell surface. Hussain et al. (2011) have shown that EV71 infection is dependent on the clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway by knockdown of the expression of proteins that participate in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. EV71 infection is also inhibited when cells are treated with drugs that block acidification of the endosome.