Figure 7.
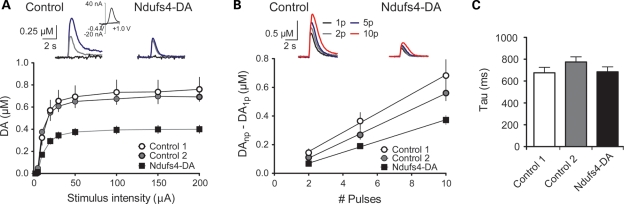
Reduced DA release in Ndufs4–DA mice. (A) Voltammetric signals elicited by single pulse stimulation at varying stimulus intensities (5, 20, and 200 μA indicated by black, gray and blue traces, respectively) in striatal slices from control and Ndufs4–DA mice. Inset of a control trace showing a typical DA cyclic voltammogram. DA release was significantly reduced across a range of stimulation intensities in Ndufs4–DA mice relative to controls (P < 0.001, two-way RM-ANOVA). Note that controls did not differ from each other, indicating that the presence of the DAT-cre construct alone did not alter DA release. (B) Voltammetric signals elicited by 25 Hz stimulation (1, 2, 5 or 10 pulses). Summary plot demonstrates the relationship between DA release and pulse number. Ndufs4–DA mice showed significantly reduced DA release relative to both control groups (P< 0.01, one-way ANOVA, Neuman–Keuls post hoc). (C) Summary of decay time constants (tau), measured from voltammetric signals. No significant differences were observed among the groups (P = 0.28, one-way ANOVA), indicating that the uptake was not affected by Ndufs4 deletion in DA neurons.